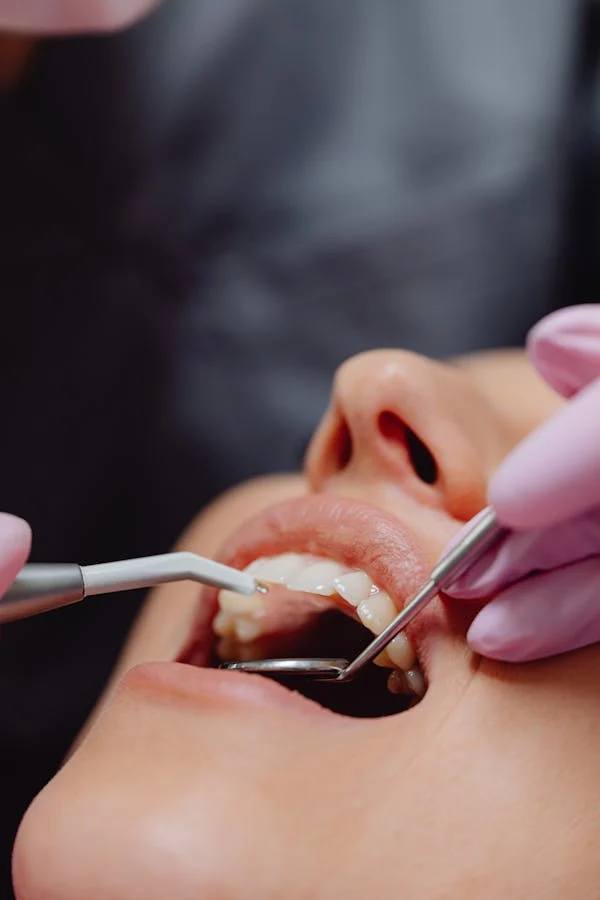
Tooth dislocation
Tooth dislocation is an injury in which the tooth is displaced relative to its normal anatomical position. The pathological condition develops with intense mechanical impact on the tooth tissue. Too intense, which exceeds the functional and natural protective capabilities of the dentition. Dislocation is a serious injury and an emergency dental condition, since without sufficient assistance there is a risk of tooth loss. And this is at least, there is always a risk of damage to adjacent tissues (teeth, periodontium, and more).
The Tooth dislocation is accompanied by severe pain and significant limitations of the dental functions. It is provided by dental therapists or dental surgeons . . Contingent on the countryside and sternness of matter harm.
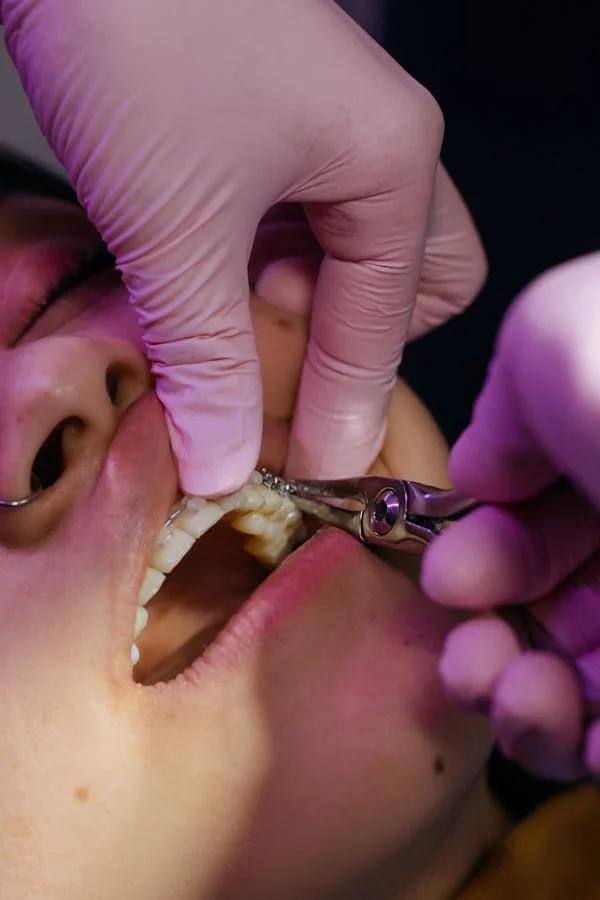
Causes of tooth dislocation
The causes of trauma are always mechanical. They are caused by excessive physical impact on the tissues of the dental row. The mechanical impulse affects a certain point (then one tooth suffers) or an area of the dental row (then a whole group of teeth suffers). Pathological conditions are not very common in dentistry. In the structure of dental pathologies and Tooth dislocation, dislocations make up no more than 8% of the total number of clinical cases. However, in the structure of injuries, dislocations account for a third of situations that require urgent care.
Meaningful the meticulous causes of tissue impairment is actual imperative. The doctor understands the nature of the injury more quickly, which means he can develop treatment methods more effectively and quickly. Moreover, every hour counts when dislocating. It also becomes possible to develop individual secondary prevention measures.
Direct culprits of injury
The tooth Dislocation in the socket relative to the normal anatomical position develops for several mechanical reasons.
The first is gnawing on inappropriate objects. Using teeth for other purposes. When cutting nut shells or opening bottles, the likelihood of injury is highest. The question here is not whether an injury will occur – it will definitely happen. The only question is when. Caries and incisors are most often injured, since they have only one root. But there are options. The other cause is a direct blow to the tooth area. During a fight, a traffic accident (for example, when hitting the steering wheel or dashboard). The concentration of the impression during a traffic accident is usually such that the damage affects several teeth. Combined injuries often develop: fractures, dislocations, jaw damage, etc.
The third reason is iatrogenic. It is related with the activities of the medic. The tooth shifts relative to its normal position against the background of the extraction of complex teeth. Most often, we are talking about either a truly difficult clinical case or the insufficient qualification of the doctor, the inexperience of the specialist, which is also possible.
All the above reasons can be prevented in one way or another. Choose a competent dentist, drive carefully, do not get into fights and do not use your teeth for their intended purpose. It’s all quite simple.
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis is in one way or another connected with excessive mechanical impact on teeth. Usually the order of trauma development is as follows:
- physical impact, usually in a straight line, at an angle – very rarely, and its intensity significantly increases the stability of the periodontium, periodontium and the tooth itself (both the crown part and the root);
- violation of the integrity of the ligamentous apparatus? periodontal injuries, periodontal disease;
- development of a local hematoma: it creates a mass effect that pushes the tooth outward, beyond the gum;
- Tooth dislocation: exit beyond the alveolus or complete loss, tooth tissue may be preserved, or it may be damaged (the same pulp, neurovascular bundle of the tooth).
In maximum belongings, the pathogenesis of the illness is the similar. Only the immediate causes of the development of the pathological process differ.
Increased risk factors
Certain conditions increase the possibility of tooth dislocation. But do not directly cause the grievance. These contain:
history of hypovitaminosis and avitaminosis.
playing sports, especially contact sports (martial arts and others), when there is a high probability of being hit in the face, in the jaw area;
childhood, milk teeth are not so well fixed;
teenage years, due to the nature of activity, tendency to risky behavior;
careless eating, especially fruit (damage can also occur when chewing);
poor oral hygiene;
And these are far from all the possible risk factors. Bad habits play a big role, for example. Smoking, alcohol abuse.
Elderly patients are also at risk. However, the reason here is not the patient’s advanced age, but the concomitant pathology. The overwhelming majority of people over 50 (and sometimes 5-10 years earlier) develop clinical signs of periodontitis or periodontosis. They are not so obvious and pronounced. Therefore, patients do not rush to see a doctor until the clinical picture becomes too pronounced and intense.
When it is no longer possible not to notice, then patients turn to specialists. A decrease in the strength of the periodontium, its functions creates risks of tooth mobility. If it previously happens the force obligatory to disturb a tooth from its opening is much a smaller amount than what is usually required. And then an injury can develop from ordinary chewing of even not very hard food (for example, an apple or other fruits, vegetables, fibrous products).
According to our estimates, such cases of dislocations occur in almost 25% of the total number of clinical situations.
Dentist-therapist
Classification and types of tooth dislocations
Classification of dislocations is carried out depending on the nature of the changes and the severity of the injury.
Depending on the nature of the injury, there are three types of dislocations:
- complete dislocation of the tooth;
- incomplete dislocation of a tooth (also known as subluxation);
- impacted or intrusive dislocation of a tooth.
A whole displacement, as the designation proposes, is escorted by the tooth deteriorating out of the opening. This is the most severe injury. But if you act quickly, the tooth can be saved and provide a sufficient clinical result, restoring the dentition without complex manipulations.
Incomplete damage is accompanied by Tooth dislocation, tissue damage, but the dislocated unit does not fall out of the socket, does not leave the row. It only changes its location and orientation relative to the normal axis (rotation – torsion is possible, for example).
The impacted type of dislocation is accompanied by the penetration of the affected tooth, its pressing into the socket. The damage is severe, but in terms of recovery, the most favorable. Then such grievances habitually go away on their own. Another way of classification is based on the extent and severity of the injury. There are 3 types of dislocation:
- isolated, develops frequently, accompanied by Tooth dislocation without significant damage to other tissues;
- with damage to periodontal or periodontal tissues, a more severe version of tissue damage and bruxim ;
- combined trauma, when dislocation provokes fractures and dislocations of the jaws and other teeth, develops with a large force of negative mechanical impact on tissues (in a traffic accident, falling from a great height).
Organization of the compulsive Tooth dislocationhelps to improved understand the countryside of the harm and develop the needed corrective measures.
Symptoms of tooth dislocation
Symbols of tooth disarticulation rest on on the type of impairment. There are specific manifestations that help to better recognize and understand the Tooth dislocation.
In circumstance of partial disarticulation or subluxation, the tooth is only to some extent exiled. Relative to its business & course in the erect, flat plane. Often both are present. The tooth looks out of place, goes beyond the socket, lengthens, interfering with normal bite.
In case of comprehensive disarticulation, the tooth waterfalls out totally. The socket is empty. Local bleeding often develops. Including quite intense bleeding (and if there are coagulation Tooth dislocation, it is very dangerous). The tooth can be saved only in some cases.
In case of intrusion or impacted fracture the tooth is shortened. Tooth dislocation comes out of the bite, but in a different way, compared to incomplete dislocation. The pathological condition is accompanied by pronounced clinical symptoms, which intensify when opening the mouth.
There are also general symptoms that are present in one way or another with any tooth dislocation. These are:
- pain, painful sensations are intense or extremely intense, sometimes so much so that they cause traumatic shock (although this is a fairly rare occurrence), the pain intensifies when opening the mouth, chewing, trying to speak;
- disruption of chewing function, not just one tooth suffers, but the patient’s entire dental system;
- formation of a hematoma, the tooth becomes bluish, possible damage to the gum structure;
- if the loss is incomplete, the tooth becomes loose and mobile;
- turbulences of standard mouthful, that is blocking concluding of teeth;
- pronounced distortions of the dentition and face variations in the ovoid and delineation.
Other pains also develop. In the face area, the entire jaw.
Important!
Often the injury is not isolated, but complex. In this case, symptoms of one or another secondary injury appear. For example , a breakage of the alveolar development or a interrupted jaw. The clinical picture becomes more pronounced and diverse. All pathological conditions require treatment at once. And the more damage, the more difficult the task.
Complications of the Tooth dislocation
Complications of Tooth dislocation develop very often, and without treatment their probability is 100%. They can affect the tooth, can be periodontal and not only. Amid the possible bad penalties:
- rupture of the ultimate of the tooth and the birthplace. If the summit is split, repair is signposted, if the root is dented, the tooth is indifferent. Since there is no extensive a fortuitous for rebuilding &there is no point in the doctor’s exertions either, the tooth will not hold without support anyway;
- root resorption, resorption of the root area of the tooth, occurs when fixed in an incorrect position and when a secondary inflammatory process develops in the root zone;
- fixing a tooth in an incorrect position leads to a huge number of disorders: from changes in bite to incorrect diction;
- curvature and deformation of the root;
- death of the pulp, neurovascular bundle, in which case the tooth most often cannot be saved or reimplantation with filling of the root canals is performed;
- periodontitis, an inflammatory process in the area of the tooth ligament, periodontium (the inflammation is initially traumatic in nature, but then a bacterial component also joins in).
Ultimately, a person risks losing a tooth. Children often develop problems with the growth of permanent teeth. Also, without treatment, persistent malocclusions develop.
Difficulties can be prevented by correcting the disease and giving effective help in a dental office built for the task.
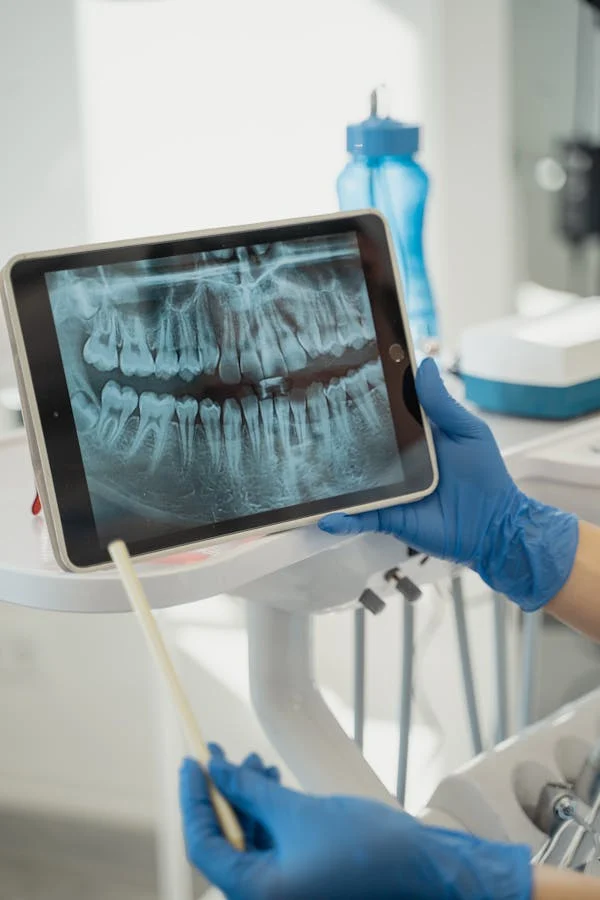
Diagnosis of tooth dislocation
Diagnosis of the pathological condition does not present any significant difficulties. A characteristic diagnosis can be made based on visual and other clinical data. The tooth is displaced or completely missing. It is mobile, held by residual intact tissues, displaced by physical impact, etc. It is much more difficult to determine secondary Tooth dislocation. It is necessary to understand how much the tooth and surrounding tissues are injured, what the complications are, whether there are any at all. This aids to mature a handling plan& if possible excluding the tooth. A assembly of procedures is charity for conclusion and ample impost. The examination is based on:
- oral survey;
- collection of anamnesis;
- visual assessment, examination of the oral cavity;
- targeted x-ray of the affected area;
- examination of the surrounding teeth to identify possible complex lesions of the segment of the dentoalveolar system (an orthopantomogram and overview image are performed).
This is regularly sufficient for judgment and taxation of the condition. If compulsory, the doctor prescribes additional check measures.
Treatment of tooth dislocation
How to treat a tooth dislocation is decided by a doctor who will evaluate the specific clinical case. Treatment is conceded out conditional on the landscape of the wrong.
In case of partial dislocation or subluxation, the task is to return the tooth to its normal anatomical position. The tooth is fused. Chronic to the prior situation is made underneath local anesthesia. To fix the affected unit, splinting is performed. Flexible structures and special threads that are highly durable are most often used for splinting teeth in case of dislocation. Fixation is performed for up to several weeks or months. Remedial is watched. As soon as the condition normalizes, the splint is removed. If the impairment is substantial, flexible or copper buildings are every so often used.
In case of complete dislocation, since the tooth falls out completely, the situation is more complicated. If it is possible to return it to its place, that is, reimplant it, this is the solution the doctor resorts to. Most often, reimplantation is suitable if the tooth has retained the pulp, it has not died, and there is no pronounced damage to the surrounding tissues. The tooth is returned to its place, splinting is performed. Repeated engraftment of the natural tooth takes up to several weeks.
Please note!
The chances of tooth recovery during reimplantation are not 100%. This is outstanding to the variations that happen in the materials. To increase the chances of recovery, a quality result, the tooth must be properly preserved. For this, special solutions are used (available in pharmacies) or regular milk. The tooth is placed in a favorable environment immediately, due to which negative changes slow down. You can put the tooth behind the cheek or under the tongue. It is significant to closely access a registrar. Otherwise, everything else is pointless. The above measures can be considered first aid for tooth dislocation.
Even with successful reimplantation, the risk of an autoimmune reaction remains for 6-24 months. The figure may elect that the tooth is a extraneous body. Intense inflammation will begin.
If the crown part is broken, but the root is preserved, most often restoration does not make sense. After that, the issue of prosthetics is decided.
In case of impacted dislocations, when the tooth shortens instead of falling out, the treatment is relatively simple. The tooth itself tends to return to its normal position. The doctor’s task is to provide rest. Do not allow the affected tooth to be loaded. The result is achieved through a gentle regimen, which is carefully worked out by a specialist. Every single week or two, a regulator X-ray is taken to evaluate the class of recovery and the effectiveness of conservative measures. If they are ineffective, surgical correction is possible. The tooth is refunded to its regular situation compulsorily, physically.
Symptomatic treatment is mandatory. A hematoma forms in the affected area, the place swells and becomes painful. Most often, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, some pain relievers and antibiotics for a long period are given. This action helps reduce risks of problems and improves symptoms of the health condition. .
Prognosis and prevention of tooth dislocation
The prognosis hinge on not only on the type of grievance . Its severity but also on the second of communicating a doctor. If a characteristic pathology develops, immediate contact with a specialist is indicated. Every hour counts. The ideal solution is to contact a doctor within the first 6 hours of receiving the injury. Then the prognosis becomes more vague. No one will guarantee a high-quality recovery. Repositioning teeth in case of dislocation, restoration of the rad may be an impossible task. Then the tooth is removed. The issue of prosthetics is decided.
Prevention is quite simple, including the following measures:
- avoiding injuries;
- Players should always use good safety practices.
- giving up bad habits.
When you get injured, you need to act as quickly as possible. This is prevention not of dislocation, but of its complications.