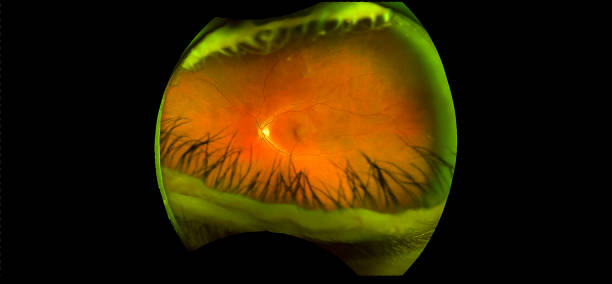
Retinal abiotrophy is a heterogeneous group of hereditary diseases of a dystrophic nature caused by gradual destruction of the retina with a decrease in visual acuity, and in some forms – complete blindness.
Symptoms are variable:
decreased visual acuity, hemeralopia and color perception disorders may be observed. Diagnosis is carried out by ophthalmological and genetic methods (ophthalmoscopy, electroretinography, fluorescent angiography, study of family history and detection of defective genes). In most forms of retinal abiotrophy, there is no specific treatment; symptomatic and supportive therapy can alleviate some symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
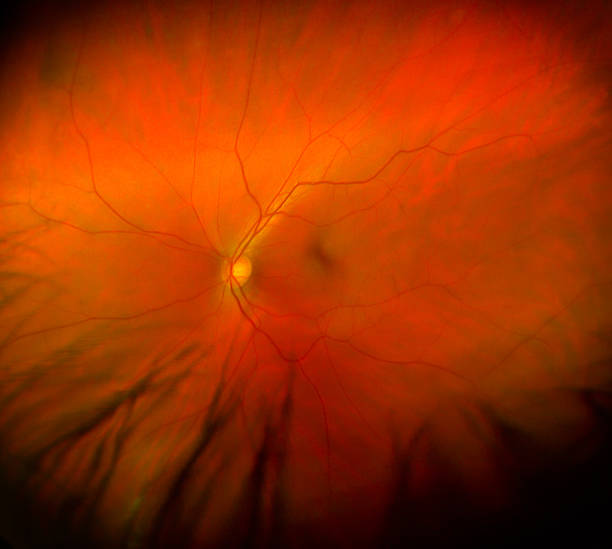
General information
Retinal abiotrophy (retinal degeneration, retinal dystrophy) is a pathology of the visual organ, in which dystrophy of the retina of the eye develops. It can be part of a symptom complex of some hereditary diseases, act as an independent pathology, in some cases secondary degeneration is possible after injuries and other impacts.
Independent hereditary forms of retinal abiotrophy have different prevalence, on average it fluctuates within 1-10:10000. For this reason, there are also strong differences in the sexual distribution of the disease – from equal affectivity of both sexes to almost complete prevalence of men among those affected (with X-linked inheritance). Genetically determined retinal abiotrophy is the most common cause of hereditary vision loss.
Reasons
Pigmentary dystrophy of the retina . The most common form of retinal abiotrophy – pigmentary dystrophy – can be caused by more than 150 mutations in several dozen genes, most of which are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Almost a quarter of all cases of pigmentary abiotrophy of the retina are caused by various mutations in the opsin protein gene. In the CRB1 photoreceptor protein gene, the mutation has a recessive inheritance pattern, and in the RP2 and RPGR genes, it is linked to the X chromosome.
There is a very rare form of pigment abiotrophy of the retina with a mutation in mitochondrial DNA and, therefore, inheritance from mother to offspring. Despite the huge number of different variants of the primary disorder in pigment retinitis ,adenoviral conjunctivitis the pathogenesis of the disease is generally the same – there is a violation of the utilization of spent rods, as a result of which they become a source of toxins in the retina. Due to the fact that the concentration of rods increases towards the periphery of the retina, pathological changes begin there, the formation of new photosensitive cells slows down, which leads to a decrease in light sensitivity.
Albuginea punctata retinalis is associated with mutations in one of four genes – RHO, PRPH2, RDH5 or RLBP1, with the most common form caused by changes in the PRPH2 gene encoding the protein peripherin. It is assumed that peripherin is involved in stabilizing the membranes of photoreceptors, mainly rods, so disturbances in its structure make them less stable and lead to their destruction. Albuginea punctata retinalis has a progressive course, with the first disturbances (which are noticeable during examination of the fundus as white dots) forming on the periphery of the retina.
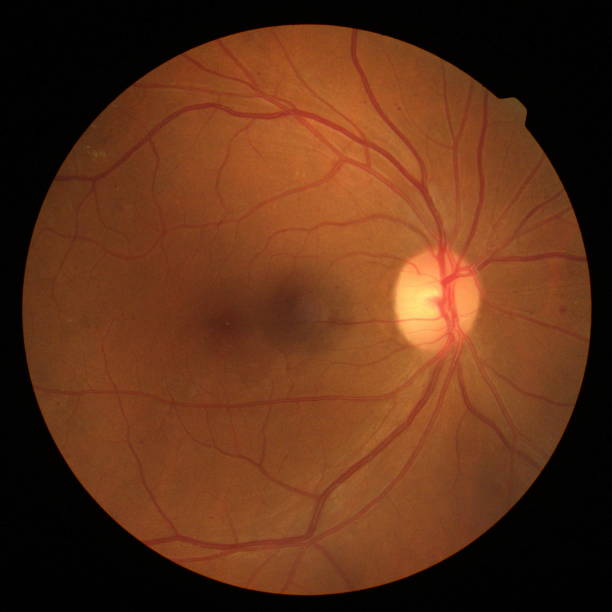
Yellow spotted retinal abiotrophy ( Stargardt disease ) is also caused by mutations in several genes. The most common form of yellow spotted retinal degeneration is associated with a disruption in the structure of the ABCA4 protein, which performs transport and energy functions in the membranes of photoreceptors. This method of the illness remains hereditary fashionable an autosomal retreating method. Changes in the structure of the transmembrane protein ABCA4 lead to the accumulation of toxic metabolites in the retina (in particular, lipofuscin), which causes dystrophy of the light-sensitive layer.
In this case, degeneration of photoreceptors is associated with a disruption in the synthesis of some components of their membranes. Another type of yellow spotted retinal abiotrophy is associated with a mutation in the PROM1 gene. The pathogenesis of disorders in this case has not been thoroughly studied.
Best’s retinal abiotrophy is caused by mutations in the BEST1 gene, the transcription product of which is the protein bestrophin, which belongs to the class of anion channels. Inheritance is autosomal dominant, the pathogenesis of the dystrophy is unknown.
Congenital stationary night blindness is a generalized retinal abiotrophy with predominant damage to the rods, it is also accompanied by other visual organ disorders – anophthalmos, strabismus , cataracts& asthenopia . Complete and incomplete forms of congenital stationary night blindness are distinguished, both are inherited by an X-linked mechanism.
The complete type is caused by a mutation of the NYX gene, which codes for a protein that ensures the transmission of excitation from rods to bipolar cells. As a result, the transmission of information from photoreceptors is disrupted, and hemeralopia occurs with almost complete lack of vision in the dark, while visual acuity and color perception are usually not affected. The incomplete form is associated with a mutation of the CACNA1F gene, the product of which is a similar protein, but it is present in both rods and cones. However, the transmission of impulses is not completely blocked, so twilight vision is only weakened, but acuity and color perception are also affected.
Classification
In ophthalmology, all hereditary forms of retinal dystrophy are divided into three groups:
- Peripheral , in which the disorders occur mainly at the edges of the fundus, but in some forms of abiotrophy they can progress and affect the central areas, up to the macula. In addition, peripheral vision suffers the most, the eye’s adaptation to darkness is impaired, glaucoma and hemeralopia often occurs.
- Central astigmatism , which are characterized by predominant damage to the macula lutea and central areas of the fundus. In this case color perception is impaired and visual acuity is greatly reduced. These are the manifestations that accompany Stargardt’s disease and Best’s disease .
- Generalized. With some mutations or their combination, retinal abiotrophy can affect the entire retina, so some researchers also distinguish a third group of dystrophies – generalized. Congenital stationary night blindness refers to this type. Generalized retinal disorders accompany other hereditary diseases – for example, Leber’s amaurosis .
At the same time, due to the large number of different mutations, the above-described division is somewhat arbitrary. Thus, some forms of pigment dystrophy can acquire a generalized character, and with a mutation of the PROM1 gene (the fourth type of Stargardt disease), abiotrophy from the central extents of the retina canister banquet to the sideline.
Symptoms of retinal abiotrophy
The symptoms of retinal abiotrophy are quite variable due to the large number of different mutations that lead to the development of this pathology. But at the same time, between different variants of dystrophy within one group (peripheral, central or generalized abiotrophies) there are a number of similar manifestations.
Peripheral retinal abiotrophies (pigmentary dystrophy, punctate abiotrophy) begin with predominant damage to the rods, so one of the first symptoms of the disease will be hemeralopia. As the pathology progresses, with further destruction of the rods, the decrease in night vision can develop into its complete loss – nyctalopia. Peripheral vision is impaired, a concentric scotoma occurs, after which the field of vision narrows so much that it becomes “tubular”.
With punctate retinal abiotrophy, more severe disorders most often do not develop, daytime vision and color perception remain unchanged. In some cases of pigment dystrophy, cones are also involved in the pathological process, which leads to a drop in daytime vision, a decrease in its acuity and sometimes complete blindness. The course of the disease can take decades, although there are also fleeting and juvenile forms.
Central retinal abiotrophies are characterized by predominant damage to cones, the highest concentration of which is in the macula lutea area – therefore they are also called macular dystrophies. The main feature is a sharp decrease in visual acuity, color perception is impaired, and with complete destruction of photoreceptors in the center of the fundus, a central scotoma develops.
If the pathological process does not spread to the peripheral areas of the retina, then peripheral and twilight vision is slightly affected. Popular forms of abiotrophy considered by pivotal hurt to photoreceptors, unsighted spots advance in the visual turf. In particularly severe forms, atrophy of the optic nerve fibers and complete blindness may occur.
Diagnostics
Patients with retinal abiotrophy should be consulted by a geneticist and an ophthalmologist . Degeneration of the retina is determined based on the results of fundus examination, electroretinography , visual acuity and color perception tests. An important role is played by studying the hereditary history, as well as genetic studies to identify mutations in genes associated with a particular type of retinal abiotrophy.
In pigment dystrophy, foci of pigment deposition are detected along the periphery of the fundus, and they can also be observed in the central areas with the corresponding form of the disease.
Which shows a piercing diminution fashionable the quantity of photoreceptors in retina. DNA sequencing to identify mutations is most often performed in relation to the RP1, RHO, RDS, RLBP1, PRPF8 genes and a number of others.
When examining the fundus, punctate retinal abiotrophy is characterized by the presence of white, sometimes metallic-tinted, foci located along the periphery of the retina. The arterioles of the retina are narrowed, dye withdrawals stand in single numbers, and the optic disc is pale. Changes in electroretinography are weakly expressed and are not a reliable diagnostic criterion. Genetic diagnostics are represented by sequencing the PRPH2 gene.
In Stargardt and Best diseases, ophthalmoscopy reveals light-colored atrophic foci, often surrounded by pigment deposits. The size and number of foci may vary significantly and reflect the severity of the retinal damage. They are mainly located in the central zones, but can also spread to the periphery. Electroretinography reveals a sharp decrease in the amplitude of wave A, indicating the predominant destruction of cones. Genetic diagnostics is reduced to identifying mutations in the ABCA4 and CNGB3 genes and studying the hereditary anamnesis.
Treatment of retinal abiotrophy
Doctors do not have any specific treatment for any type of retinal abiotrophy at this time. Vitamins A, E and riboflavin are given as treatment to help keep the disease from getting worse. A supplement with vasodilators increases blood to the retina, slowing down disease processes.
In the past few years, evidence has appeared showing that bionic retinal implants (Argus/Argus 2) have helped some people recover partial vision after their sight was lost due to abiotrophy. Experts in stem cells and gene therapy are trying to find a way to tackle retinal abiotrophy.
Forecast
Due to the large number of mutations that cause abiotrophy and the different clinical course of dystrophic processes in the retina, the prognosis is almost always uncertain. Some types of pigment dystrophy may be limited to hemeralopia and peripheral vision impairment, while other forms of this pathology lead to complete blindness. In some cases, taking vitamin A preparations can slow down the progression of retinal abiotrophy; according to some data, the use of sunglasses also allows achieving a similar result.