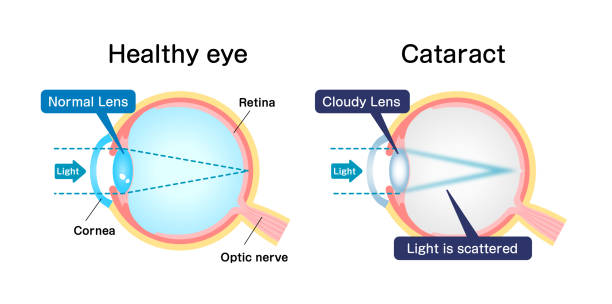
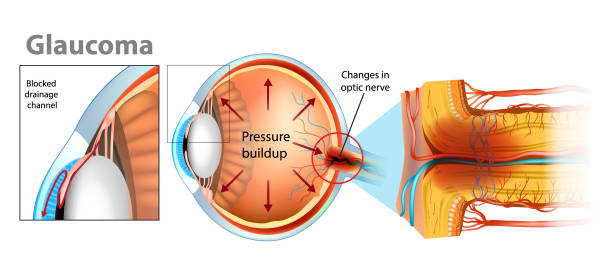
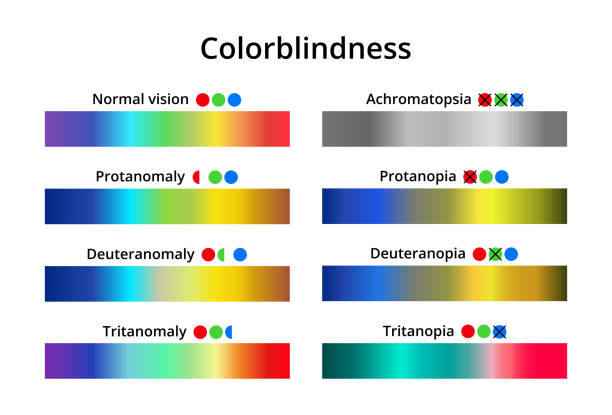
Top 3 Stages of Periodontitis and How to Treat Them Powerfully?
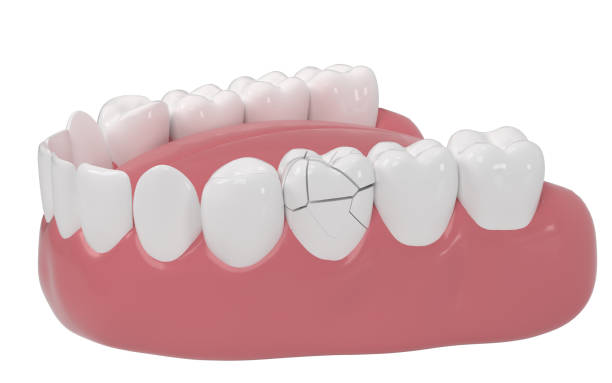
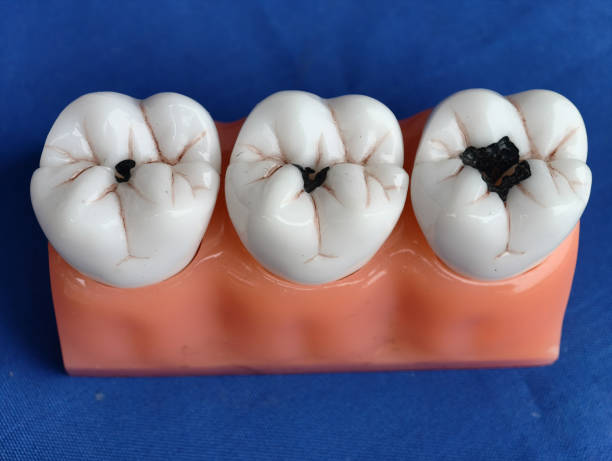
Apical periodontitis stays an irritation of the connective material (periodontium) adjoining the tooth root in the tip area. It manifests itself as sharp pain in the area of the affected…