Viral hepatitis A (Botkin’s disease) is an acute infectious liver lesion characterized by a benign course, accompanied by necrosis of hepatocytes. Viral hepatitis A is included in the group of intestinal infections, since it has a fecal-oral mechanism of infection. In the clinical course of viral hepatitis A, pre-icteric and icteric periods are distinguished, as well as convalescence. Diagnosis is made based on biochemical blood tests, RIA and ELISA results. Hospitalization of patients with viral hepatitis A is necessary only in severe cases. Outpatient treatment includes diet and symptomatic therapy.
General information
Viral hepatitis A (Botkin’s disease) is an acute infectious liver disease characterized by a benign course, accompanied by necrosis of hepatocytes. Botkin’s virus raises to viral hepatitis transferred by the fecal-oral machinery and is one of the most communal intestinal infections.
Characteristics of the pathogen
The hepatitis A virus belongs to the genus Hepatovirus, its genome is represented by RNA. The Trojan horse is pretty constant in the atmosphere persisting for several months at 4 °C and for years at 20 °C. It remains viable at room temperature for several weeks, and dies after 5 minutes of boiling. Ultraviolet rays inactivate the virus after one minute. The pathogen can remain viable for some time in chlorinated tap water.

Hepatitis A is spread by the fecal-oral appliance, mainly by rainwater and alimentary roads. In some cases, infection is possible by contact-household route when using household items and utensils. Outbreaks of viral hepatitis A with the implementation of the water route of infection usually occur when the virus gets into public water reservoirs, the food route of infection is possible both when eating contaminated vegetables and fruits, and raw shellfish living in infected water bodies. The implementation of the contact-household route is typical for children’s groups, where insufficient attention is paid to the sanitary and hygienic regime.
Natural susceptibility to the hepatitis A virus in humans is high, the greatest – in children of prepubertal age, post-infection immunity is intense (somewhat less intensity is typical after a subclinical infection) and long-term. Infection with viral hepatitis A most often occurs in children’s groups. Among adults, the risk group includes employees of food units of preschool and school children’s, as well as medical and preventive and sanatorium-resort institutions, food factories. Currently, collective outbreaks of infection are increasingly observed among drug addicts and homosexuals.
Also, extended inflammation or stress due to the infection could predispose the risk of heart-related diseases like arrhythmia, myocarditis, or hypertension risk in case of people with already present cardiovascular diseases. Although these impacts are not major characteristics of Hepatitis A, they show the necessity of early diagnosis and proper attendance.
Symptoms of viral hepatitis A
The incubation period of viral hepatitis A is 3-4 weeks, the onset of the disease is usually acute, the course is characterized by a sequential change of periods: pre-icteric, icteric and convalescence. The pre-icteric (prodromal) period occurs in various clinical variants: febrile, dyspeptic, asthenovegetative.
The febrile (flu-like) variant of the disease is characterized by a sharply developed fever and intoxication symptoms (the severity of the general intoxication syndrome depends on the severity of the disease). Patients complain of general weakness, myalgia, headache , dry cough, sore throat, irritaion , rhinitis . Catarrhal symptoms are moderately expressed, redness of the pharynx is usually not noted, their combination with dyspepsia (nausea, loss of appetite, belching) is possible .
Hepatitis A is the kind of infection of hepatitis which is basically a liver infection, but it can also indirectly affect other body systems. Among them, an example is high bilirubin concentration that can cause symptoms, among others, to the eye, such as yellowing of the eyes, and in rare patients may cause Conjunctivitis or exacerbate Cataracts in high bilirubin concentration. Mental health is no exception to the illness, as there can be long-term fatigue and an unhealthy appetite, as well as general uneasiness with accompanying Depression, Anxiety Disorders, or even Bipolar Disorder in vulnerable individuals.
The dyspeptic variant of the course is not accompanied by catarrhal symptoms, intoxication is expressed little. Patients complain primarily of duodenal syndromes, sickness, vomiting, sullenness in the mouth, belching . Dull moderate pain in the right hypochondrium, epigastrium is often noted. Disorders of defecation are possible (diarrhea, constipation , their alternation).

The pre-icteric period, proceeding according to the asthenovegetative variant, is not very specific. Patients are sluggish, apathetic, complain of general weakness, and suffer from sleep disorders . In some cases, prodromal signs are not observed (latent variant of the pre-icteric period), the disease begins immediately with jaundice. If there are signs of several clinical syndromes, they speak of a mixed variant of the course of the pre-icteric period. The duration of this phase of the infection can be from two to ten days, on average, the prodromal period usually lasts a week, gradually moving into the next phase – jaundice.
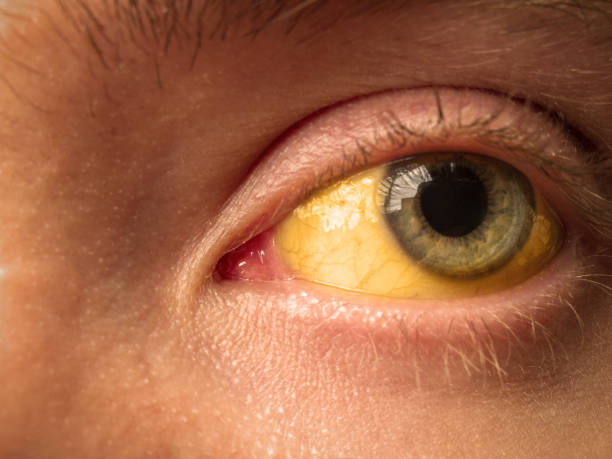
The icteric period of viral hepatitis A is characterized by the disappearance of signs of intoxication, a decrease in fever, and an improvement in the general condition of patients. However, dyspeptic symptoms usually persist and worsen. Jaundice develops gradually. At first, darkening of urine is noted, the sclera, mucous membranes of the frenulum of the tongue and soft palate acquire a yellowish tint. Later, the skin turns yellow, acquiring an intense saffron tint (hepatic jaundice).
The severity of the disease may correlate with the intensity of skin coloring, but it is preferable to focus on dyspeptic and intoxication symptoms. In severe cases of hepatitis, signs of hemorrhagic syndrome (petechiae, hemorrhages on the mucous membranes and skin, nosebleeds ) may be observed. During physical examination, a yellowish coating is noted on the tongue and teeth. The liver is enlarged moderately painful upon palpation, and in a third of cases, an enlarged spleen is noted. The pulse is somewhat slower ( bradycardia ), and blood pressure is low.
The stool becomes lighter, even completely discolored at the height of the disease. In calculation to dyspeptic sicknesses, patients may whine of asthenovegetative signs.
The duration of the icteric period usually does not exceed a month, on average it is 2 weeks, after which the recovery period begins: there is a gradual regression of clinical and laboratory signs of jaundice, intoxication, the liver size is normalized. This phase can be quite long, the duration of the recovery period usually reaches 3-6 months. The course of viral hepatitis A is mainly mild or moderate, but in rare cases severe forms of the disease are noted. Chronicity of the process and virus carriage are not typical for this infection.
Complications of viral hepatitis A
Viral hepatitis A is usually not prone to exacerbations. In rare cases, the infection can provoke inflammatory processes in the biliary system ( cholangitis , cholecystitis , dyskinesia of the biliary tract and gall bladder). Sometimes hepatitis A is complicated by the addition of a secondary infection . Severe complications from the liver ( acute hepatic encephalopathy ) are extremely rare.
Diagnosis of viral hepatitis A
A general blood test shows a decreased concentration of leukocytes, lymphocytosis, and an increased ESR. A biochemical analysis shows a sharp increase in aminotransferase activity, bilirubinemia (mainly due to conjugated bilirubin), decreased albumin content, low prothrombin index, increased sublimate and decreased thymol tests.
Specific diagnostics are based on serological methods (antibodies are detected using ELISA and RIA). In the icteric period, an increase in IgM is noted, and in the convalescent period – IgG. The most accurate and specific diagnostics is the detection of viral RNA in the blood using PCR. Isolation of the pathogen and virological testing is possible, but due to the labor intensity, it is impractical for general clinical practice.
Treatment of viral hepatitis A
Botkin’s disease can be treated on an outpatient basis, hospitalization is carried out in severe forms, as well as according to epidemiological indications. During the period of severe intoxication, patients are prescribed bed rest, diet No. 5 (in the version for acute hepatitis), vitamin therapy. Fractional nutrition, fatty foods are excluded, products that stimulate the production of bile, dairy and plant components of the diet are encouraged.
It is necessary to completely exclude alcohol. Etiotropic therapy for this disease has not been developed, the complex of therapeutic measures is aimed at symptomatic relief and pathogenetic correction. For the purpose of detoxification, copious drinking is prescribed, if necessary, infusion of crystalloid solutions. In order to normalize digestion and maintain intestinal normobiocenosis, lactulose preparations are prescribed. Antispasmodics are castoff to avoid cholestasis. If necessary, UDCA (ursodeoxycholic acid) preparations are prescribed. After clinical recovery, patients are under dispensary observation by a gastroenterologist for another 3-6 months.
In the vast majority of personal belongings the prognosis is satisfactory. In case of complications from the biliary tract, the cure is delayed, but with false therapy the prognosis is not aggravated.
Prevention of viral hepatitis A
General preventive measures are aimed at ensuring high-quality purification of drinking water sources, control over wastewater discharge, sanitary and hygienic requirements for the regime at public catering establishments, in the kitchens of children’s and medical institutions. Epidemiological control is carried out over the production, storage, transportation of food products; in case of outbreaks of viral hepatitis A in organized groups (both children’s and adults), appropriate quarantine measures are taken.
Patients are isolated for 2 weeks, their infectiousness after the first week of the icteric period disappears. Admission to study and work is carried out upon clinical recovery. Contact persons are monitored for 35 days from the moment of contact. Quarantine is prescribed for this time in children’s groups. The necessary disinfection measures are carried out in the source of infection.

Inoculation against hepatitis A is not compulsory for children ripened 1 year and elder and for adults peripatetic to areas where viral hepatitis A is a hazard.