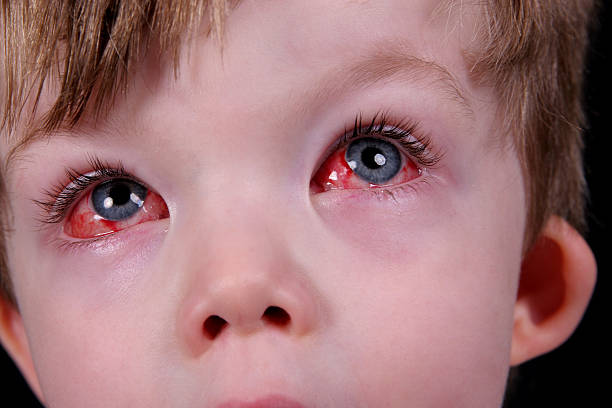
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis remains a polyetiological seditious scratch of the conjunctiva, the slippery casing lid the inside surface of the eyelids and sclera. Various forms of conjunctivitis occur with hyperemia and edema of the transitional folds and eyelids, mucous or purulent discharge from the eyes, lacrimation, burning and itching in the eyes, etc.
Diagnosis of conjunctivitis is performed by an ophthalmologist and includes: external examination, biomicroscopy, instillation test with fluorescein, bacteriological examination of a smear from the conjunctiva, cytological, immunofluorescent, enzyme immunoassay of a scraping from the conjunctiva, additional consultations (infection specialist, dermatovenerologist, ENT, phthisiatrician, allergist) as indicated. Treatment of conjunctivitis is mainly local, medicinal, with the use of eye drops and ointments, rinsing the conjunctival sac, and subconjunctival injections.
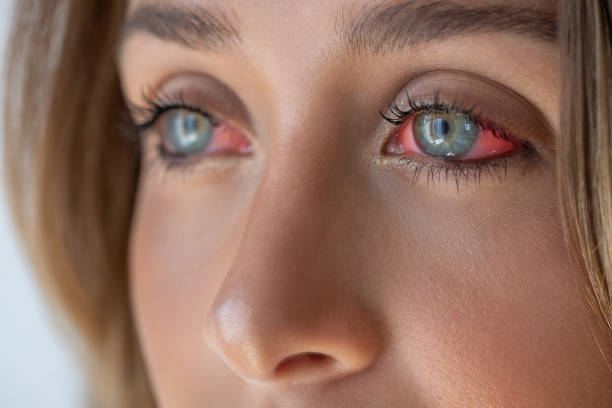

General information
Conjunctivitis is the most common eye disease – it accounts for about 30% of all eye pathology. The frequency of inflammatory lesions is associated with its high reactivity to various exogenous and endogenous factors, as well as the accessibility of the conjunctival cavity to adverse external influences. The term “conjunctivitis” in ophthalmology unites etiologically heterogeneous diseases that occur with inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane of the eye. The course can be complicated by blepharitis, keratitis, dry eye syndrome, entropion, scarring of the eyelids and cornea, corneal perforation, hypopyon, decreased visual acuity, etc.
The conjunctiva performs a protective function and, due to its anatomical position, is constantly in contact with many external irritants – dust particles, air, microbial agents, chemical and temperature effects, bright light, etc. Normally, the it has a smooth, moist surface, pink color; it is transparent, through it the vessels and meibomian glands shine through; it secretion resembles a tear. With the mucous membrane becomes cloudy, rough, and scars may form on it.

Reasons
Bacterial conjunctivitis usually occurs when infected by contact and household means. In this case, bacteria that are normally few in number or not part of the normal microflora begin to multiply on the mucous membrane. The toxins secreted by the bacteria cause a pronounced inflammatory reaction. The most common causative agents of bacterial are staphylococci, pneumococci, streptococci , Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella of infectious etiology (pneumococcal, diphtheria , diplobacillary, gonococcal ( gonoblennorrhea ), etc.)
- conjunctivitis of chlamydial etiology ( paratrachoma , trachoma )
- conjunctivitis of viral etiology ( adenoviral , herpetic , viral infections, peter abnomly, molluscum contagiosum , etc.)
- conjunctivitis of fungal etiology (in actinomycosis , sporotrichosis, rhinosporiosis, anophthalmos, coccidiosis, aspergillosis, candidiasis , etc.)
- conjunctivitis of allergic and autoimmune etiology (with hay fever , spring catarrh, conjunctival pemphigus , atopic eczema , asthenopia , demodicosis , gout , sarcoidosis , psoriasis , Reiter’s syndrome, glaucma )
- conjunctivitis of traumatic etiology (thermal, chemical)
- metastatic conjunctivitis in general diseases.
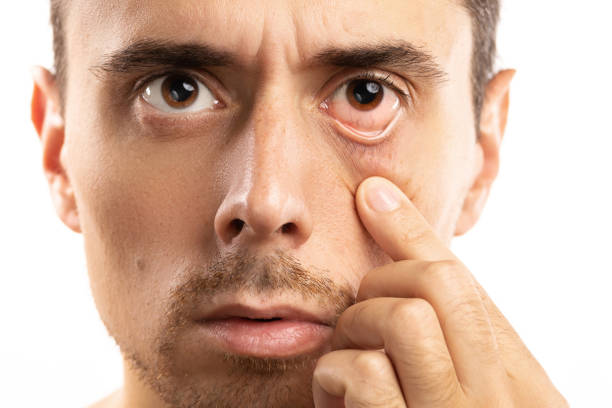

Symptoms of conjunctivitis
Specific manifestations of conjunctivitis depend on the etiologic form of the disease. However, the course of various origins is characterized by a number of common signs. These include: swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the eyelids and transitional folds; discharge of mucous or purulent secretion from the eyes; itching , burning, lacrimation, color blindness ; sensation of “sand” or a foreign body in the eye ; photophobia , blepharospasm, astigmatism.
Often the main symptom is the inability to open the eyelids in the morning due to their sticking together with dried secretions. With the development of adenoviral or ulcerative keratitis, visual acuity may decrease. With , both eyes are usually affected: sometimes inflammation occurs in them alternately and proceeds with varying degrees of severity.

Acute conjunctivitis manifests itself suddenly with pain and burning in the eyes. Contrary to the related hyperemia, bleedings remain habitually well-known. Conjunctival injection of the eyeballs, swelling of the mucous membrane are expressed ; abundant mucous, mucopurulent or purulent secretion is released from the eyes. With acute , general well-being is often impaired: malaise, headache, and increased body temperature appear.
Severe conjunctivitis canister previous since one toward two or three weeks. Subacute conjunctivitis remains considered through less pronounced symptoms than the acute form of the disease. Chronic conjunctivitis develops gradually, and its course is persistent and long-term. Discomfort and a sensation of a foreign body in the eyes, rapid eye fatigue, moderate hyperemia and looseness which takes on a velvety appearance, are noted. Keratitis often develops against the background of chronic conjunctivitis.
A specific manifestation of bacterial etiology is a purulent, opaque, viscous discharge of a yellowish or greenish color. Pain syndrome, dry eyes and skin around the eyes are noted.
Viral conjunctivitis often occurs against the background of upper respiratory tract infections and is accompanied by moderate lacrimation, photophobia and blepharospasm, scanty mucous discharge, submandibular or parotid lymphadenitis. In some types of viral eye lesions, follicles or pseudomembranes form on the mucous membrane of the eye.
Allergic usually occurs with severe itching, aching in the eyes, lacrimation, bump of the eyelids, from time to time allergic rhinitis besides cough, atopic eczema.
The clinical features of fungal conjunctivitis are determined by the type of fungus. Actinomycosis causes cataract or purulent conjunctivitis; blastomycosis causes membranous with grayish or yellowish easily removable films. Candidiasis is characterized by the formation of nodules consisting of a cluster of epithelioid and lymphoid cells; aspergillosis occurs with it hyperemia and corneal damage.
it caused by toxic chemicals causes severe pain when moving the eyes, blinking, or trying to open or close the eyes.
Diagnostics
Conjunctivitis is diagnosed by an ophthalmologist based on complaints and clinical manifestations. To determine the etiology , anamnesis data are important: contact with patients, allergens, existing diseases, connection with the change of season, exposure to sunlight, etc. Outdoor scrutiny discloses hyperemia then edema of the conjunctiva, inoculation of the eyeball, the company of liberation.
To establish the etiology , laboratory tests are carried out: cytological examination of a scraping or smear-print, bacteriological examination of a smear from the conjunctiva, determination of the titer of antibodies (IgA and IgG) to the suspected pathogen in the tear fluid or blood serum, and a study for demodex. In case of allergic , skin-allergic, nasal, and sublingual tests are used.
If a specific etiology is detected, a consultation with an infectious disease specialist , venereologist, or phthisiatrician may be required; in the case of an allergic form of the disease, an allergist; in the case of a viral form, an otolaryngologist. Of the special ophthalmological examination methods used for it, biomicroscopy of the eye , fluorescein instillation test , etc. are used. Conjunctivitis is also caused Myopia .
Differential diagnostics of its is carried out with episcleritis and scleritis , keratitis, uveitis (iritis, iridocyclitis, choroiditis), acute attack of glaucoma , foreign body in the eye, canalicular obstruction in dacryocystitis.
Treatment of conjunctivitis
The conduct schedule meant for conjunctivitis is arranged by an ophthalmologist, pleasing interested in version the pathogen the severity of the process and existing complications. Topical treatment requires frequent rinsing with medicinal solutions, instillation of medicinal products, application of eye ointments , and subconjunctival injections .
In case of this, it is forbidden to apply bandages to the eyes, since they impair the evacuation of discharge and can contribute to the development of keratitis. To avoid autoinfection, it is recommended to wash your hands more often, use disposable towels and napkins, separate pipettes and eye sticks for each eye.
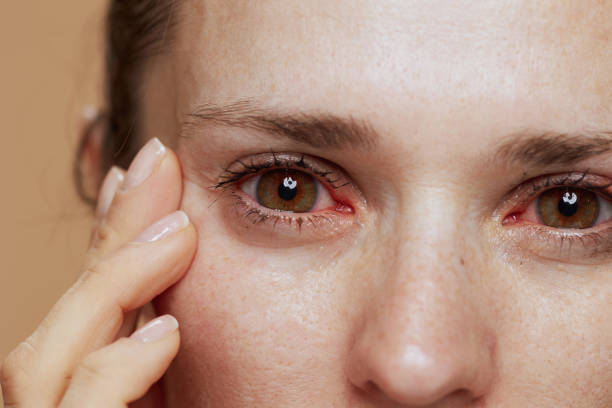
Before introducing medications into the conjunctival cavity, local anesthesia of the eyeball is performed with solutions of novocaine (lidocaine, trimecaine), then – toilet of the eyelash edges of the eyelids, and eyeball with antiseptics (solution of furacilin, potassium permanganate). Until information about the etiology of conjunctivitis is obtained, a solution of sulfacetamide is instilled into the eyes, and eye ointment is applied at night.
If bacterial etiology is detected, gentamicin sulfate is used locally in the form of drops and eye ointment, erythromycin eye ointment. Virusostatic and virucidal agents are used to treat viral conjunctivitis: trifluridine, idoxuridine, leukocyte interferon in the form of instillations and acyclovir – locally, in the form of ointment, and orally. Antimicrobial drugs can be prescribed to prevent the addition of a bacterial infection.
If chlamydial conjunctivitis is detected, in addition to local treatment, systemic administration of doxycycline, tetracycline or erythromycin is indicated. Therapy for allergic includes the administration of vasoconstrictor and antihistamine drops, corticosteroids, artificial tears, and desensitizing drugs. For conjunctivitis of fungal etiology, antimycotic ointments and instillations are prescribed (levorin, nystatin, amphotericin B, etc.).
Prevention Timely and adequate therapy allows for recovery without consequences for visual function. In incident of lesser hurt to the cornea, idea could be situated compact. The main prevention is compliance with sanitary and hygienic requirements in medical and educational institutions, compliance with personal hygiene standards, timely isolation of patients with viral lesions, and implementation of anti-epidemic measures.
Prevention of chlamydial and gonococcal in newborns involves treatment of chlamydial infection and gonorrhea in pregnant women. In case of a tendency to allergic conjunctivitis, preventive local and general desensitizing therapy is necessary on the eve of the expected exacerbation.