Atrial fibrillation ( AF) refers to a heart rhythm, which shows a high frequency of uncoordinated excitation of some heart chambers atria as well as uncontrolled contraction of the atria or twitch of small groups of atrial heart muscle fibers. The rate of the heart in AF is 350-600 per minute. In the case of long-term paroxysm of AF (more than 48 hours), thrombosis and ischemic stroke are observed. In the presence of permanent AF, one can count on a sudden development of chronic circulation failure.
General information
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a rhythm disturbance of the heart which is manifested in the frequent irregular excitation and contraction of the atria or twitching, fibrillation of separate parts of atrial muscle fibers. The AF heart rate goes to 350-600 beats per minute. The chance of developing thrombosis and ischemic stroke rises, with a long-lasting paroxysm of AF (more than 48 hours). In a persistent type of AF, an acute development of chronic circulatory failure is evident.
Atrial fibrillation is one of the most common types of rhythm disturbances and accounts for up to 30% of hospitalizations due to arrhythmias . The frequency of atrial fibrillation escalations with age; it follows in 1% of patients above 60 a month of Sundays of age and in more than 6% of patients over 60 years of stage of development.

Reasons
Both cardiac pathology and diseases of other organs can lead to the development of atrial fibrillation. Most often, accompanies the course of myocardial infarction , cardiosclerosis , rheumatic heart defects , myocarditis , cardiomyopathy , arterial hypertension , severe heart failure and Coronary Artery Aneurysm. Sometimes it occurs with thyrotoxicosis , intoxication with adrenergic drugs, cardiac glycosides, alcohol, and can be provoked by neuropsychic overload, hypokalemia.
Idiopathic atrial fibrillation also occurs, the causes of which remain undetected even with the most thorough examination.
Pathogenesis
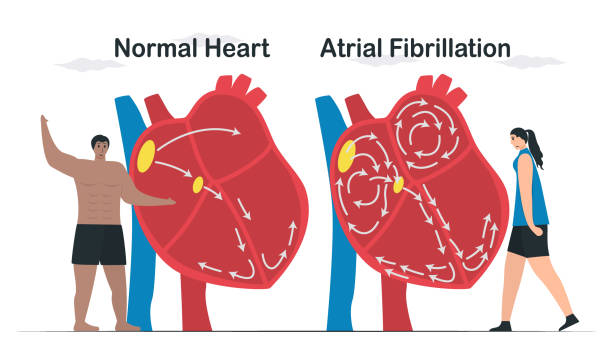
Atrial flutter is a rapid (up to 200-400 per minute) contraction of the atria while maintaining a correct coordinated atrial rhythm. Myocardial contractions during atrial flutter follow one another almost without interruption, there is almost no diastolic pause, the atria do not relax, being in a state of systole most of the time. Big the atria through blood is difficult, and, therefore, the flow of plasma into the ventricles declines. During atrial fibrillation, individual groups of muscle fibers contract, resulting in a lack of coordinated contraction of the atrium.
A significant number of electrical impulses are concentrated in the atrioventricular junction: some of them are delayed, others spread to the myocardium of the ventricles, causing them to contract with different rhythms. According to the frequency of ventricular contractions, tachystolic (ventricular contractions of 90 or more per minute), normosystolic (ventricular contractions from 60 to 90 per minute), bradystolic (ventricular contractions less than 60 per minute) forms are distinguished.
During a paroxysm , there is no pumping of blood into the ventricles (atrial supplement). The atria contract ineffectively, so during diastole the ventricles are not completely filled with blood flowing freely into them, as a result of which there is periodic failure to eject blood into the aortic system.
Every 2nd, 3rd or 4th impulse can come to the ventricles via the atrioventricular connections, providing the correct ventricular rhythm – this is correct atrial flutter. When atrioventricular conduction is disrupted, chaotic contraction of the ventricles is observed, i.e. an incorrect form of atrial flutter develops.
Classification
The modern approach to the classification of atrial fibrillation is based on the nature of the clinical course, etiological factors and electrophysiological mechanisms.
There are permanent (chronic), persistent and transient (paroxysmal) forms . In the paroxysmal form, the attack lasts no more than 7 days, usually less than 24 hours. Persistent and chronic atrial fibrillation last more than 7 days, the chronic form is determined by the ineffectiveness of electrical cardioversion. Paroxysmal and persistent forms can be recurrent.
A distinction is made between a newly diagnosed attack of atrial fibrillation and a recurrent attack (second and subsequent episodes of atrial fibrillation). It can occur in two types of atrial rhythm disorders: atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter .
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation
The manifestations of atrial fibrillation depend on its form (bradystolic or tachystolic, paroxysmal or constant), the condition of the myocardium, the valve apparatus, and the individual characteristics of the patient’s psyche. The tachystolic form of atrial fibrillation is much more difficult to bear. In this case, patients experience rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, which increases with physical exertion, pain, and interruptions in the heart.
Usually, it initially occurs in attacks, the progression of paroxysms (their duration and frequency) is individual. In some patients, after 2-3 attacks of atrial fibrillation, a persistent or chronic form is established, in others, rare, short-term paroxysms with no tendency to progression are observed throughout life.
The onset of a paroxysm of atrial fibrillation may be felt in different ways. Some patients may not notice it and learn about the arrhythmia only during a medical examination. In typical cases, it is felt by chaotic heartbeats, sweating, weakness, tremors, fear, polyuria. With an excessively high heart rate, dizziness, fainting , and Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attacks may be observed . Symptoms of its disappear almost immediately after the sinus heart rhythm is restored. Patients suffering from a permanent form of atrial fibrillation eventually stop noticing it.

During auscultation of the heart, irregular tones of varying volume are heard. An arrhythmic pulse with different amplitudes of pulse waves is determined. With a pulse deficit is determined – the number of minute contractions of the heart exceeds the number of pulse waves). The pulse deficit is due to the fact that not every contraction of the heart ejects blood into the aorta. Patients with this diseases feel palpitations, shortness of breath, sometimes discomfort in the heart area, pulsation of the veins of the neck.
Complications
The most common complications are thromboembolism and heart failure . In mitral stenosis complicated by it, blockage of the left atrioventricular orifice by an intra-atrial thrombus can lead to cardiac arrest and sudden death.
Intracardiac thrombi can enter the system of arteries of the systemic circulation, causing thromboembolism of various organs; 2/3 of them enter the cerebral vessels with the blood flow. Every 6th ischemic stroke develops in patients with it . Patients over 65 years of age; patients who have previously suffered thromboembolism of any localization; those suffering from diabetes mellitus , systemic arterial hypertension , congestive heart failure are most susceptible to cerebral and peripheral thromboembolism .
Mind failure with atrial fibrillation changes in patients misery from heart defects and weakened ventricular contractility. Heart failure with mitral stenosis and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can manifest itself as cardiac asthma and pulmonary edema . The development of acute left ventricular failure is associated with impaired emptying of the left chambers of the heart, which causes a sharp increase in pressure in the pulmonary capillaries and veins.
One of the most severe manifestations of heart failure in atrial fibrillation may be the development of arrhythmogenic shock due to inadequately low cardiac output. Trendy some cases it may advancement to ventricular fibrillation and cardiac capture. Most often, chronic heart failure develops , progressing to arrhythmic dilated cardiomyopathy .
Diagnostics
Typically, atrial fibrillation is spotted by now during a animal checkup. When palpating the peripheral pulse, a characteristic irregular rhythm, filling and tension are determined. When auscultating the heart, irregular heart sounds are heard, significant fluctuations in their volume (the volume of the first tone following the diastolic pause changes depending on the magnitude of diastolic filling of the ventricles). Patients with detected changes are referred to a cardiologist for consultation .
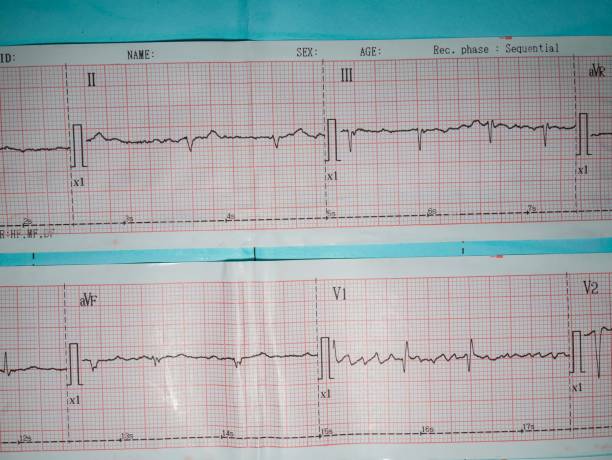
Confirmation or clarification of the diagnosis of atrial fibrillation is possible using electrocardiographic data. In atrial fibrillation, the ECG does not show P waves that record atrial contractions, and the ventricular QRS complexes are located chaotically. In atrial stake, atrial rollers are spotted in dwelling of the P wave.
With the help of daily ECG monitoring , the heart rhythm is monitored, the form of atrial fibrillation, the duration of paroxysms, their connection with loads, etc. are specified. Physical exercise tests ( bicycle ergometry , treadmill test ) are carried out to identify signs of myocardial ischemia and when selecting antiarrhythmic drugs.
Echocardiography allows determining the size of the heart cavities, intracardiac thrombi, signs of damage to the valves, pericardium, cardiomyopathy, and assessing the diastolic and systolic function of the left ventricle. EchoCG helps in making decisions about prescribing antithrombotic and antiarrhythmic therapy. Meticulous meditation of the heart can be reached consuming MRI or MSCT of the heart .
Transesophageal electrophysiological study ( TEECG ) is performed to determine the mechanism of development of atrial fibrillation, which is especially important for patients who are scheduled for catheter ablation or implantation of a pacemaker (artificial pacemaker).
Treatment of atrial fibrillation The choice of treatment tactics for various forms of atrial fibrillation is aimed at restoring and maintaining sinus rhythm, preventing repeated attacks of atrial fibrillation, monitoring heart rate, and preventing thromboembolic complications. To stop paroxysms of atrial fibrillation, it is effective to use novocainamide (intravenously and orally), quinidine (orally), amiodarone (intravenously and orally), and propafenone (orally) under the control of blood pressure and electrocardiogram.
A less pronounced result is achieved by using digoxin, propranolol and verapamil, which, however, by reducing the heart rate, contribute to the improvement of the patient’s well-being (reduction of shortness of breath, weakness, sensations of palpitations). In the absence of the expected positive effect from drug therapy, they resort to electrical cardioversion (application of a pulsed electrical discharge to the heart area to restore the heart rhythm), which stops paroxysms of atrial fibrillation in 90% of cases.
With atrial fibrillation lasting more than 48 hours, the risk of thrombus formation increases sharply, therefore, warfarin is prescribed to prevent thromboembolic complications. To prevent recurrence of atrial fibrillation attacks after restoration of sinus rhythm, antiarrhythmic drugs are prescribed: amiodarone, propafenone, etc.
When establishing a chronic form of atrial fibrillation, continuous intake of adrenergic blockers (atenolol, metoprolol, bisoprolol), digoxin, calcium antagonists (diltiazem, verapamil) and warfarin (under control of coagulogram parameters – prothrombin index or INR) is prescribed. In case of atrial fibrillation, treatment of the underlying disease that led to the development of rhythm disturbance is mandatory.
A method that radically eliminates atrial fibrillation is radiofrequency isolation of the pulmonary veins, during which the focus of ectopic excitation located in the mouths of the pulmonary veins is isolated from the atria. Radiofrequency isolation of the mouth of the pulmonary veins is an invasive technique, the effectiveness of which is about 60%.
In case of frequently recurring attacks of atrial fibrillation or its permanent form, it is possible to perform RFA of the heart – radiofrequency ablation (“cauterization” with an electrode) of the atrioventricular knob with the design of a widespread sloping AV block and imbedding of a stable pacemaker .
Forecast
The main prognostic criteria for atrial fibrillation are the causes and complications of the rhythm disturbance. Atrial fibrillation caused by heart defects, severe myocardial lesions (large-focal myocardial infarction, extensive or diffuse cardiosclerosis, dilated cardiomyopathy) quickly leads to the development of heart failure.
Thromboembolic complications caused by atrial fibrillation have an unfavorable prognosis. Atrial fibrillation increases mortality associated with heart disease by 1.7 times.
In the absence of severe cardiac pathology and a satisfactory condition of the ventricular myocardium, the prognosis is more favorable, although frequent occurrence of paroxysms of atrial fibrillation significantly reduces the quality of life of patients. With idiopathic atrial fibrillation, well-being is usually not impaired, people feel practically healthy and can perform any work.
Prevention
The goal of primary prevention is the active treatment of diseases that are potentially dangerous in terms of the development of atrial fibrillation (arterial hypertension and heart failure).
Secondary prevention measures for atrial fibrillation are aimed at following recommendations for anti-relapse drug therapy, performing cardiac surgery , limiting physical and mental stress, and abstaining from alcohol consumption.