Astigmatism
An abnormal non spherical shape of both the cornea & lens leads to astigmatism. That’s what happens, making the light rays scatter and resulting in a distorted picture on the retina. If astigmatism rises above 1 diopter, it causes visual problems, problems seeing clearly, headaches, quick exhaustion when focusing, irritation around the eyebrows. The symptoms of astigmatism are identified by an ophthalmologist following testing of visual acuity, refraction, ophthalmoscope use, examining the eye with a biomicroscope, measuring intraocular pressure, using an eye ultrasound and computer keratotopography. For astigmatism, glasses and contact correction, laser correction with LASIK, astigmotomy and phakic lens implant can be used.
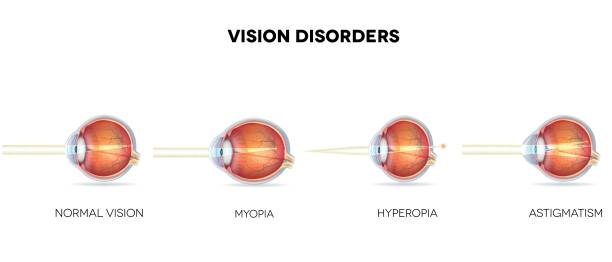
General information
Astigmatism, along with myopia and hyperopia , is related in ophthalmology to the so-called ametropias – conditions characterized by a change in the refractive power of optical media and distortion of the back focus of the eye. Among all types of ametropia, astigmatism occurs in 10% of cases. Early correction of astigmatism is the key to successful prevention of amblyopia and strabismus .
Through astigmatism, by way of effect of the desecration of the unvarying bend (sphericity) of the cornea or lens. Their external has an unfit refractive authority in different meridians, so the beam of rays does not converge at one point on the retina, as is normal. In some cases, the image is focused on the retina, but in the form of a segment, a blurred ellipse or a “figure eight”; in others – behind or in front of the retina. The image seen by a person with astigmatism becomes distorted, blurry and unclear.
Causes of astigmatism
The cause of astigmatism is a violation of the configuration of the optical system of the eye – uneven curvature of the cornea or an irregular shape of the lens. In most cases, astigmatism is an inherited pathology of vision, often associated with congenital uneven pressure of the eyelids, extraocular muscles and bones of the orbit on the membranes of the eye. Therefore, if one of the parents in the family suffers from astigmatism, the child should be examined by an ophthalmologist as early as possible.
Acquired astigmatism can develop in adults as a result of cicatricial changes in the cornea that occur as a result of eye injuries ,glaucoma, ophthalmological surgeries, adenoviral conjunctivitis dystrophic processes ( keratoconus ), corneal opacity, cataracts and inflammation (keratitis).

Types of astigmatism
Depending on the refraction of the main meridians (perpendicular planes of the eye), a distinction is made between direct astigmatism (with the greatest refractive power of the vertical meridian), reverse astigmatism (with the greatest refractive power of the horizontal meridian), and with oblique axes.
By type, there are regular and irregular astigmatism. With regular , the two main meridians are mutually perpendicular; with irregular , they are located obliquely. Regular is divided into simple, in which one of the meridians has normal refraction – emmetropia; complex, characterized by the same refraction (myopia or hypermetropia) in both meridians; mixed through diverse categories of deflection in the zeniths. When combined with myopia, they speak of myopic astigmatism , with farsightedness – of hypermetropic astigmatism .
Depending on the time of occurrence near congenital (correct) and acquired (incorrect) . Congenital within 0.5 to 0.75 D is considered physiological. Acquired is always pathological.
According to the latter feature, a weak degree (up to 3 Dptr), an average degree (3-6 Dptr) and a high degree (above 6 Dptr) of distinguished.
When the refractive power of the cornea is incorrect, when there is a refractive defect in the lens, we speak of crystalline astigmatism.
Symptoms of astigmatism
As a rule it manifests itself in preschool or first institute stage. A child with astigmatism may confuse similar letters or change their places in words, complain of poor vision, distortion and blurriness of vision of objects, frequent headaches , unpleasant sensations in the superciliary region. it is characterized by asthenopia, manifested in rapid visual fatigue, a feeling of “sand” in the eyes; intolerance to wearing glasses, which requires their frequent replacement.
Symptoms of astigmatism are not very specific; in the early stages, the disease often manifests itself as a slight blurring of vision, so it is often mistaken for eye fatigue. Warning signs that may indicate loss of visual clarity, when objects appear uneven, deformed, blurry; pain, redness, conjunctivitis, burning in the eyes; double vision with increased visual strain (when reading, working at a computer), difficulty in visually determining the distance to objects, etc.
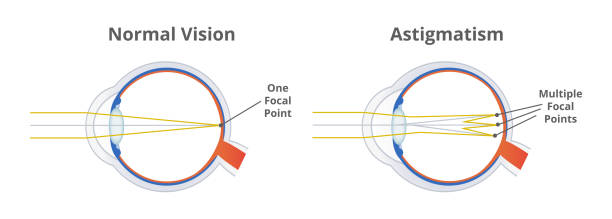
Diagnosis of astigmatism
An ophthalmologist consultation if it is suspected includes a comprehensive assessment of the state of visual function, examination of the eye structures, refraction testing , and indirect visualization methods.
Visual acuity testing ( visometry ) for its is performed without correction and with correction. In the latter case, the patient is given a trial frame in which one eye is covered with an opaque screen, and cylindrical lenses of different refractive power are placed in front of the other, achieving maximum visual acuity.
The degree of refraction is determined using skiascopy (shadow test) with spherical lenses and cylindrical (astigmatic) lenses (cylindroskiascopy). More complete information about refractive error is provided by refractometry , performed in a state of mydriasis (pupil dilation).
In order to determine the probable causes (inflammatory or degenerative diseases of the cornea) , biomicroscopy of the eye is performed ; to exclude pathology of the fundus and vitreous body, ophthalmoscopy is performed . The anterior posterior section of the eye remains inspected with ophthalmometry in addition ultrasound of the eye .
The presence and degree , as well as the detection of keratoconus, is carried out using computer keratotopography .
Treatment of astigmatism
To treat astigmatism, specs, communication lenses, laser and microsurgical correction are used. Ophthalmological correction is indicated for astigmatism of more than 1 diopter, progressive decrease in visual acuity, symptoms of anophthalmos , and increasing degrees of farsightedness or nearsightedness.
Spectacle correction is provided by individual selection of glasses (usually complex), which combine spherical and cylindrical lenses. Spherical lenses are selected according to the rules for correcting hyperopia or myopia, the refractive power of the cylindrical lens must match the degree of astigmatism. With a high degree , wearing complex glasses can be accompanied by dizziness, eye pain, and visual discomfort.
An alternative to glasses for astigmatism correction is to use toric (astigmatic) contact lenses. The advantage of contact correction is that the lens, unlike glasses, forms a single optical system with the eye and does not cause spatial distortions. Orthokeratological (night) lenses can be used for minor it. Periodic repeated consultations with an ophthalmologist are necessary to correct glasses and contact lenses. However, both glasses and lenses can only temporarily correct vision defects, but cannot completely eliminate astigmatism.
In case of myopic or mixed it, intolerance to glasses correction, impossibility of laser correction and different refraction in the meridians, astigmotomy ( keratotomy ) is indicated – a procedure of making microcomputer cuts on the cornea, which allows weakening the strong meridian at the periphery. In case of hypermetropic , laser & thermokeratocoagulation can be performed cauterization of the margin of the cornea snowballing its convexity then refractive control.
In recent years, excimer laser correction using the LASIK method has played a leading role in the treatment of astigmatism. It is indicated for up to ±3-4 D. The practice designed intended for laser rectification of it remains done on an casualty foundation by means of resident drop anesthesia.
During the correction, a special microkeratome device is used to separate the superficial layer of the cornea with a thickness of 130-150 microns, then a laser is used to evaporate part of the cornea to a certain depth in clearly defined areas, after which the exfoliated flap is returned to its place. Suturing is not performed with this method of its correction, since the epithelium along the edge of the flap is restored on its own. Improvement in vision after excimer laser correction is noted within 1-2 hours after the end of the procedure, and final recovery occurs within a week.
In the postoperative period, it is recommended to limit physical and visual loads, protect the eyes from injury, and avoid thermal procedures (visiting a sauna , taking hot baths). Eye drops (with dexamethasone, an antibacterial and moisturizing component) are prescribed, and a repeat examination by an ophthalmologist is required. In the future, it may be recommended to undergo hardware treatment ( laser stimulation , video computer training), take special vitamin preparations for the eyes, undergo courses of eye exercises, massage of the neck and collar zone, hydroprocedures, etc.
If excimer laser correction of its high degree is not possible, phakic lenses are implanted .
Forecast and prevention of astigmatism
If it is not treated in a timely & adequate manner a sharp decrease in visual acuity, amblyopia and strabismus may develop. The criteria for a high-quality correction are an improvement in the quality of binocular vision.
Prevention consists of rational distribution of visual loads, their alternation with special exercises for the eyes and physical activity, prevention of injuries and inflammation of the cornea. To detect congenital astigmatism, it is necessary to conduct a medical examination of children in accordance with the age schedule.