Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia in children is a disturbance of the normal functioning of the heart, which is accompanied by disturbances in the frequency and regularity of myocardial contractions. The pathological condition is common, mainly in young children and adolescents. In many cases, the disorders do not manifest themselves with specific symptoms. The signs accompanying arrhythmia are easily mistaken for symptoms of another disease, most often, due to inattention, the manifestations are attributed to vegetative-vascular dystonia, and this is a very serious misconception. Rhythm disturbances can be dangerous. Mainly due to the likelihood of cardiac arrest and brain damage, ischemic processes in the central nervous system.
Diagnosis and treatment of arrhythmia is the work of a pediatric cardiologist. Treatment is complex. It includes changing the regimen, using special antiarrhythmic drugs and medications to normalize blood pressure.
Causes of the development of rhythm disturbances
The causes of rhythm disturbances can be congenital or acquired. The past remain further common than second. Mostly, there are myocardial malformations, valve disorders (aortic, tricuspid, mitral). According to statistics, rhythm disturbances are present in almost 15% of patients in the younger age group. Most of them are relatively mild disorders, but there are also life-threatening disturbances of conduction, excitability, and automatism of the heart. They are most often discovered by chance, which creates additional risks. Treatment should begin as early as possible, and without determining the cause of the pathology, this is impossible. Diagnostics are carried out using instrumental methods under the supervision of a specialist.
Pathogenesis of the disorder
The pathogenesis of the disturbance of the frequency and regularity of contractions is very different. There are main options:
- violation of cardiac automatism: the trendsetter, the so-called sinus bump, is in charge for myocardial contractility. This one is a small cluster of specific cells in the right atrium. Gamble its work is disrupted, an irregular rhythm develops;
- disorders of myocardial tissue excitability, the impulse from the pacemaker is conducted to the ventricles and atria, but if the tissue is not capable of normal excitability, for example, with abundant scarring, contractions will be irregular and chaotic;
- conduction disturbances, the transmission of the impulse from the pacemaker occurs through special bundles (His, Bachmann), the distribution of the impulse occurs through the atrioventricular (AV) node, coronary artery diseases, if the conduction system is damaged for some reason, the signal simply will not reach the other chambers of the heart.

The causes of arrhythmia, heart damage in a child can be both cardiac and extracardiac. The former are more common. Among the possible problems:
- previous cardiac interventions;
- congenital and acquired heart defects;
- history of myocarditis, inflammatory processes of the heart of infectious and autoimmune nature;
- electrolyte imbalances as a result of past infections, as well as while taking certain medications (diuretics, hormonal drugs).
There are also extracardiac causes of rhythm changes. Among them:
- prematurity, in which case rhythm disturbances can be both temporary and permanent;
- blood pathologies, including iron deficiency anemia, as the main form of the disorder;
- diseases of the endocrine system and functional, temporary hormonal imbalances (the hormones of the adrenal cortex and thyroid gland are especially important in this regard);
Determining the causes of a pathological condition is the job of a cardiologist. If symptoms develop, you should contact him as soon as possible. If there are no visible manifestations, you should undergo a medical examination once a year until you reach adulthood.
Factors that increase the risk of disorder
Influences that increase the probability of emergent the disease contain:
- prematurity, if the baby was born prematurely, the heart failure, most often the rhythm normalizes as the patient develops;
- the neonatal period, as well as the age up to 14 years, are the peak periods of development of pathological rhythm disturbances;
- excessive physical exertion is a factor in the development of cardiomyopathy, a change in the condition of the myocardium when it grows and loses normal contractility;
- hypertrophy of the ventricles, atria, for the same reason, the contractility of the heart becomes insufficient;
- blood pressure surges, the idea that they only occur in adults is incorrect, this is not true, in some cases hypertension occurs in children, this is not normal, treatment is required;
- female gender, cases of rhythm disturbances are more common in girls and young women due to hormonal background;
- Chronic diseases of the endocrine and central nervous systems can manifest themselves in unexpected ways.
Risk factors can be eliminated. This will reduce the risks of pathological changes.
Classification and types of arrhythmias
Classification or division of arrhythmias into types is carried out according to the degree of severity, type, nature of changes, and presence of symptoms.
The most informative division is by the nature of the changes. In this case, three groups of changes can be distinguished.
The chief cluster remains a desecration of automatism. That stands, the exertion of the sinus protuberance. Rhythm disorders of this kind include:
- skating times;
- sinus bradycardia: once the sum of blows turn out to be a smaller amount than the age average;
- sinus tachycardia, in which case there are too many contractions;
- sinus arrhythmia, alternating disturbance, sometimes tachycardia, sometimes bradycardia.
Migration of the pacemaker is possible when the sinus node is responsible for the contraction, and different areas of the heart, which poses a serious danger.
The second group of disorders are myocardial excitability disorders. The following types of arrhythmia are distinguished:
- extra systole : once the blows trail arrhythmic ally outdoor the main arrangement
- atrial fibrillation, chaotic contraction of the four chambers of the heart, there is a possibility of cardiac arrest, therefore the condition is extremely dangerous;
- paroxysmal tachycardia, differs from sinus frequency by its chaotic contractions, the heart rate can reach 180 beats or more.
Such forms of disorders are much more dangerous than the first group. The third group is cardiac conduction disorders. The following are distinguished:
- intra-atrial blocks;
intraventricular blocks; - sinoatrial forms of conduction disturbances;
- atrioventricular blocks.
Often, rhythm irregularities are of a mixed nature. Several types of irregularities are observed at once..
Please note!
Another classification of symptoms is present . Accordingly, symptomatic and asymptomatic forms of arrhythmia are distinguished. Symptomatic disorders of the cardiovascular system manifest themselves clearly. There are clinical signs, although often non-specific. This one is terrible to type a finding built on them. Asymptomatic ones do not give any clinical manifestations and this is their danger. However, according to our statistical estimates, they are common. Almost half of clinical cases. About 5-8% are severe disorders that are dangerous for the child’s life.
Degrees of severity of rhythm disorder
The degree of expression is a generalized indicator of the severity of the pathological process. It is not very informative. It is more accurate to use the criteria of the severity of a specific pathological process (for example, AV block 1, 2, 3 degrees, etc.). But it gives an idea of the severity of the pathological processmild arrhythmia in a child, when symptoms are absent or appear from time to time, after very intense physical activity;
- moderate arrhythmia in a child, which manifests itself more clearly, with regular symptoms or objective signs that are visible on the ECG;
- severe arrhythmia in a child, manifesting itself with severe symptoms or pronounced manifestations on the ECG, often significantly reducing the quality of life, requiring radical treatment.
With a degree rating, the disorder can be assessed to choose the best ways to carry out further diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of the disorder
The disorder manifests itself in different ways. The pathological process is accompanied by a non-specific clinical picture. Simply put, it is simply impossible to determine that the rhythm disorder is to blame. Diagnostics is required. Among the signs of arrhythmia in children:
- shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air;
- decreased physical activity, the child plays and runs less than his peers;
- pale skin, increased sweating;
- blueness of the nasolabial triangle or cyanosis is a typical symptom of impaired nutrition and oxygen supply to the myocardial tissues, which occurs with moderate and severe arrhythmias;
- complaints of headache, dizziness, weakness;
- tendency to faint.
Important!
Respiratory disorders with arrhythmia in children, cardiovascular manifestations, neurological disorders. Here is a triad of symptoms that can lead to thoughts about arrhythmia or other cardiac dysfunction. If there is even the slightest suspicion of heart problems, you need to see a cardiologist as soon as possible.
Complications of rhythm disturbances
The main complication, which is also the most dangerous, is asystole, cardiac arrest. There are enough known cases when an apparently healthy child died during physical education classes at school after intense physical activity. Other possible problems are delays in physical and mental development due to insufficient tissue nutrition. Because with arrhythmia, the heart often cannot provide nutrition and oxygen even to itself. Not to mention the body tissues. Timely treatment of the disorder is the only effective measure to prevent complications.
Diagnosis of pathological condition
Diagnostics, detection of cardiac arrhythmias in children is carried out by instrumental methods. At the initial appointment, the specialist interviews the patient and his parents. Assesses the nature of the disorders. Collects anamnesis, listens to the tones and rhythm of the heart (auscultation). Prescribes objective examination measures:
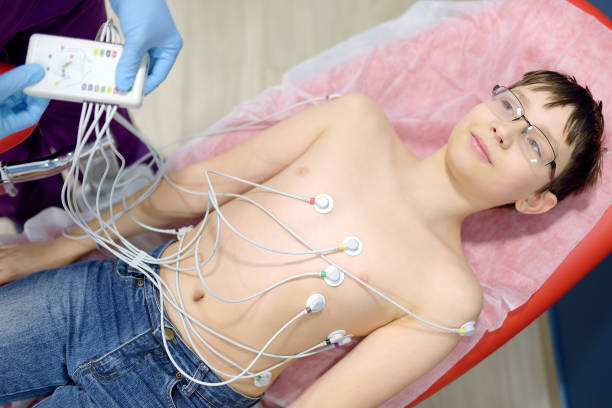
- ECG often allows us to identify significant disorders, but in severe cases, when arrhythmias manifest themselves from time to time, the technique is not informative enough;
- 22-hour ECG monitoring consents you near clasp intricate, periodically occurring forms of the disorder. Since the cardiogram is taken throughout the day;
- blood pressure measurement;
- Ultrasound of the heart or ECHO to determine the pressure in large vessels, their general condition, the condition of the myocardium and its structures;
- EEG to rule out central nervous system damage;
- functional and stress tests, because some forms of arrhythmia manifest themselves only during physical exertion.
Laboratory tests may also be performed, such as blood tests for hormones.
Treatment methods for the disorder
Basically, clinical recommendations insist on complex therapy of the pathological process. The task is to change the daily routine, physical activity, and vitaminization of the diet. Symptomatic methods include the use of drugs to increase myocardial contractility, antiarrhythmic drugs, and drugs to normalize blood pressure.
In some heart defects, conduction disorders, treatment is surgical. The operation container stand performed by means of a minimally invasive way or open access, reliant on the precise judgment.
Treatment stands accepted at home or in hospital. In case of severe arrhythmia in a child, hospitalization and emergency care are needed.
Pathology prognosis
Prognosis depends on the type of pathology. The severity of the disorder & the timeliness of medical care. If the disorder has been detected, this is an important measure and more than half the success.
Prevention of pathological process
There is no specific prevention. Because there are too many pathologies and they differ in nature, their origin. Universal recommendations are simple: proper pregnancy management, quality nutrition, timely treatment of diseases in the child, as well as regular preventive examinations under the supervision of a cardiologist. At least once a year. For patients from the risk group (premature babies, children after infection, teenagers 12-14 years old, newborns) – 2 times a year.