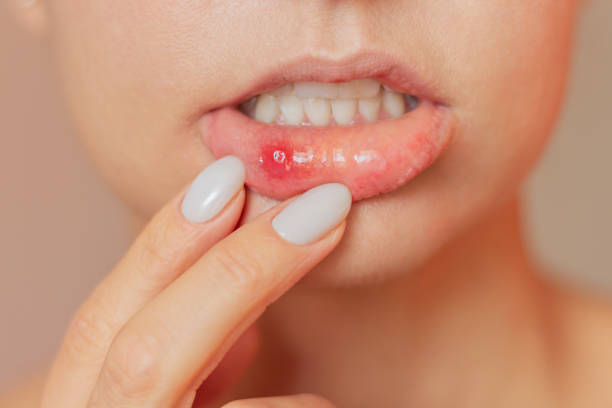
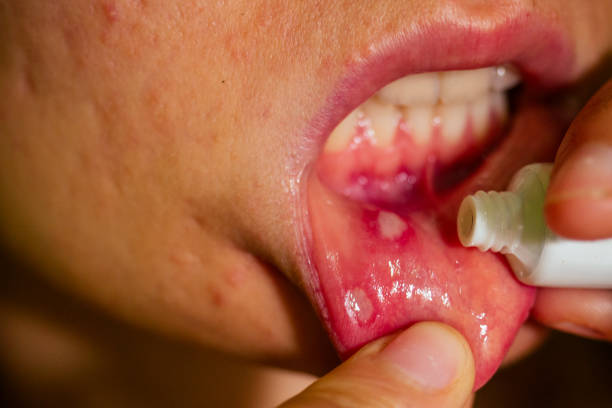
Aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the tissues of the oral cavity. This form is quite common, it is second in prevalence, second only to catarrhal stomatitis. The disease is characterized by the appearance of whitish or yellow ulcers, papules in the oral cavity. Favorite localization is the cheeks, mucous membranes of the lips. It can appear on the tongue. Often the localization is multiple, there are single aphthae – it depends on the aggressiveness of the infectious agent, as well as on the activity and intensity of the body’s immune response. Aphthous stomatitis is tremendously painful and necessitates appropriate conduct.
Improvement of the sickness is accepted available underneath the direction of dentist. Local antiseptic drugs are needed.
Causes of aphthous stomatitis
According to research, up to 20% of the world’s population suffers from the disease, and relapses are more common in women and children. The course of the disease is unstable and uneven. It is possible to develop both a single inflammation and a recurrent form of the process. In the latter case, ulcers and aphthae form regularly. The sickness returns up to several times.
The causes of the disease are considered mixed, combining infectious and allergic mechanisms. The disease is often associated with immune disorders, infections and environmental factors. It can be said that the etiology of aphthous stomatitis is multifactorial. This is a consensus opinion. Research, however, continues.
Immediate causes of the disease
Aphthous stomatitis develops under the influence of various factors. The disease has a mixed nature. Its immediate triggers are often infectious agents, allergens or various pathologies of internal organs.
Infections are one of the key causes of aphthous stomatitis. The inflammatory pathology is provoked by a whole group of pathogens:
- herpes viruses: types 1 and 2;
- bacteria: most often staphylococci and streptococci;
- Fungi: are quite rare as pathogens, with Candida fungi playing a special role in the process.
Allergic reactions play a major role. Acute inflammatory process develops as a consequence of:
- food allergies, most often triggered by citrus fruits, chocolate, nuts or hot spices, they have the greatest allergenic potential;
- some medications: antibiotics, painkillers can cause an allergic reaction with characteristic manifestations of gum ;
- Dental materials: Antipathies to metals secondhand in contents and dentures can cause aphthous eruptions.
Please note!
The appearance of aphthae is often associated with the course of chronic internal diseases. Internal diseases: hormonal disorders, gastrointestinal pathologies, deficiency of vitamins and microelements. These factors also provoke the disease, and if the patient already suffers from aphthous stomatitis, they aggravate the course of the disease.
Pathogenesis of the disease
The development of a pathological condition depends on the nature of the disease – infectious or allergic. In both cases, local inflammation plays a key role.
The infectious mechanism is particularly common. It includes a whole group of components:
- penetration of infection: pathogens, viruses, bacteria or fungi penetrate through microtraumas of the mucous membrane or are activated from a latent state when immunity is reduced;
- failure of the immune system to rise to the challenge: a weakened immune system doesn’t do its job in suppressing the pathogen when it is still new;
- inflammation: conversation boosts the number of inflammatory cytokines which greatly affects surrounding tissues.
- starting at this stage, harmful microbes infect and start to replicate in the cells on the surface of the nose, causing changes and damaging them, while local vascular problems in the area may disrupt blood flow and lead to a swelling of the mucous membrane.
- formation of ulcers, at the site of infection penetration aphthae are formed – superficial ulcers surrounded by inflamed hyperemic tissue;
- In case of fracture teeth aphthous stomatitis produced.
- subduing infectious organisms and calming inflammation: the activation of immune cells such as macrophages and lymphocytes, dampens the infection, the inflammation eases, ulcerations heal and the tissue is reduced or mucous membrane, is restored.
- In case of allergy the mechanism is similar. Only inflammation starts not because of infection, but because of false immune reaction, autoimmune inflammation.
Risk factors for the development of pathology
The mostly unknown causes differ by person, but a number of factors raise the odds of developing aphthous stomatitis. They do not straight cause the development of raw ulcers. However, they significantly increase the likelihood of the disorder. Possible risk factors include:
- genetic predisposition, negative heredity;
- infectious diseases: viral infections in the past can lead to extra medical risks;
- Gastrointestinal infections or disease can result in damage to the lining inside your mouth.
- having a deficiency of important vitamins and minerals.
- submitting to allergens: some patients having allergic reactions to certain substances;
- stress: prolonged nervous tension or chronic stress conditions are characterized by additional danger;
- a history of herpes infection, since it is chronic and almost completely incurable, the likelihood of aphthous stomatitis is always there;
- colds: regular episodes of acute respiratory viral infections or flu contribute to a weakening of the general immune system;
- bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol and poor oral hygiene;
- eating under-processed food: unwashed fruits and vegetables can become a source of pathogenic microorganisms;
- thermal burns;
- immune and hormonal disorders: both natural and pathological;
- previous injuries to the oral cavity: become a gateway for pathogenic microorganisms;
- systemic diseases: blood diseases, tuberculosis, HIV, etc.;
- a sharp change in climate: the body’s adaptation to new climatic conditions can temporarily weaken the immune system;
- poor hygiene: dirty hands, etc., these factors are especially common among children.
Many risk factors can be adjusted. Medical help is indicated.
Classification and types of disorder
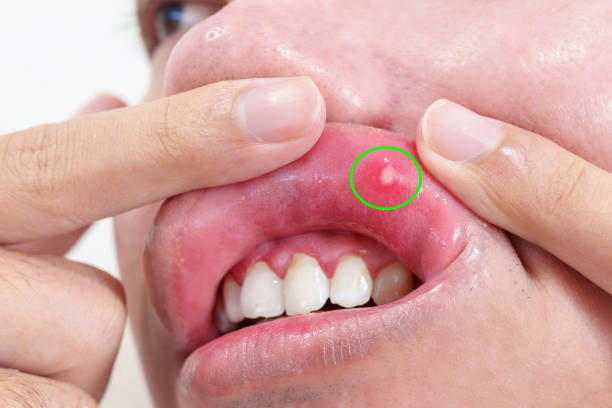
The disease is classified according to various criteria: the nature of the course, the severity and the predominant symptoms. A thorough classification helps to determine the approach to treatment.
If the division is carried out along the flow, the following are distinguished:
- acute aphthous stomatitis: symptoms develop suddenly, often against the background of infections or allergic reactions, accompanied by pronounced symptoms, pain, swelling and general discomfort;
- fchronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis: accompanied by periodic exacerbations and long-term remissions, occurs suddenly, its course is often difficult to predict, associated with immune or systemic disorders.
If we classify the disorder by the degree of severity, we can name it:
- mild form, lesions are isolated, small in size, symptoms are minimal, discomfort occurs only when eating or brushing teeth;
- moderate form: multiple aphthae are typical, the disease manifests itself with local symptoms, moderate pain syndrome, difficulty in eating and talking develops;
- severe form: large ulcers, severe inflammation and severe pain, general symptoms often appear, fever, weakness.
The division is carried out according to the predominant symptom. The following are distinguished:
- fibrinous aphthous stomatitis: small ulcers covered with a grayish coating form on the mucous membrane; this is the most common form of the disease;
- necrotic aphthous stomatitis: tissue necrosis occurs in the area of the ulcers, this stomatitis is typical for patients with severe immune or systemic disorders;
- cicatricial aphthous stomatitis: aphthae heal with the formation of scars, often affecting the deep layers of the mucous membrane;
- glandular aphthous stomatitis: affects the ducts of the salivary glands, manifested by painful ulcers;
- lichenoid aphthous stomatitis: resembles lichen planus, with characteristic white stripes on the background of inflamed mucous membrane, the nature of ulcers, the degree of discomfort varies from case to case;
- deforming aphthous stomatitis: a severe form in which, after the ulcers have healed, changes in the structure of the mucous membrane are observed, bruxim often requiring surgical correction after the acute inflammation has subsided.
Arrangements help the doctor calculate the brutality of the sickness, pick the finest therapy and prevent possible difficulties.
Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis
There are signs of aphthous stomatitis in adults and children that are always present.
Formation of aphthae is typical. Small oval or round ulcers appear on the mucous membrane. You container realize a clear control to aphthae, with the superiority being protected in a red, engorged border and a bleached or gray coating. Many ulcers are found on the insides of the cheeks, lips, below the language or on the appetite.
Patients notice a hot sensitivity in their openings at the foundation of the disease
. These symptoms develop before ulcers appear.
There is pain. Severe pain syndrome when eating, talking, swallowing. The pain intensifies when the ulcers come into contact with sour, spicy or hot food.
There is swelling and redness. Around the aphthae and in other areas of the mucous membrane, swelling and hyperemia, redness are often observed.
Often, the general condition worsens. In severe cases, the body temperature rises, weakness and fatigue appear. These are signs of general intoxication of the body.
General symptoms such as pain and bad breath describe the typical average clinical picture. However, the aphthous form of stomatitis manifests itself differently, depending on the form and severity of the pathological process. Several characteristic features can be identified. In the mild form, lone ulcers of unimportant size up to 5 mm are shaped. There are minimal general symptoms, discomfort is limited to the oral cavity in the area of ulcer formation.
In moderate severity of the disease, multiple aphthae are present, the ulcers are larger, up to 10 mm. There is noticeable difficulty in eating and talking. The worst for patients is with a severe form of inflammation. Large ulcers and deep lesions of the mucous membrane are formed. General symptoms are pronounced, an increase in temperature to 38-39 ° C is possible.
According to our estimates, mild or moderate forms develop most often. They respond well to therapy.
Dentist-therapist
The chronic form of aphthous stomatitis has no symptoms. During the reduction old-fashioned, there are no indications. During an exacerbation, the clinical picture corresponds to the picture of an acute inflammatory process. The formation of new erosions and exacerbation of the pathological condition occur suddenly and with varying frequency. In theory, they can be prevented. This requires competent prevention.
Complications of the disease
Complications occur quite rarely. Mainly in the absence of timely treatment or against the background of predisposing factors. Amongst the undesirable significances that may occur:
- chronization of the process;
- periodontal disease with the potential for tooth loss;
- development of necrotic stomatitis;
- systemic complications up to and including blood poisoning, but this is a very rare occurrence.
To avoid problems, you should consult a doctor and not wait to do so. The likelihood of complications is quite low, but it is not completely zero. It is not worth risking your health.
Diagnosis of aphthous stomatitis
Diagnosis of acute or recurrent aphthous stomatitis with chronic course requires a thorough approach. Among the measures:
- oral survey to identify complaints and symptoms;
- collecting anamnesis: identifying possible factors that provoked the disease;
- examination of the oral cavity, visual assessment of the condition of the oral mucosa, identification of aphthae, their location, size and appearance;
- laboratory tests: complete blood count: to detect signs of inflammation or anemia, additional tests include vitamin levels, nutrients, iron levels, vitamin B12 and folate;
- Allergy testing: to determine the possible allergic nature of the disease;
Using a microbiological examination, doctors may scrape from the surface of the aphthae and test for microorganisms
- immunological tests;
- histological examination.
The meticulous list of trainings is strong-minded by a dentist-therapist. Sometimes differential diagnostics is required. Distinguishing aphthous stomatitis from other forms of stomatitis, periodontal diseases, herpetic tissue lesions. Only a specialist can differentiate disorders and make an accurate diagnosis. You won’t be able to do anything on your own.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
Treatments for acute aphthous stomatitis are intended to ease inflammation, stop infection from spreading and speed healing of the mucous membrane.. The basis of therapy is medication. The following group of drugs is indicated:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- moutheswashes that kill germs;
- remedial medications that hurry the renewal of the slimy skin;
- drugs that relieve pain;
- immunomodulators, prescribed for severe course of the pathological process;
- Antihistamines: to reduce the intensity of inflammation in any form of aphthous stomatitis.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis requires a mandatory change in diet. Gentle nutrition plays an important role in treatment. It is necessary to avoid irritating food: spicy, sour, hot or too hard. It would not be superfluous to include soft and easily digestible products in the diet: soups, purees, porridges. Mandatory consumption of products rich in vitamins B, C and E is indicated. They are needed to prevent hypovitaminosis and avitaminosis, activate the immune response and regenerative processes.
Important!
In severe forms of aphthous stomatitis, the formation of large aphthae, necrotic changes, pronounced deformations, surgical removal of the affected areas or necrotic tissues is indicated. The operation is performed with subsequent treatment with antiseptic and healing agents. This is an extreme measure, but sometimes it alone can change the situation.
Treatment of chronic aphthous stomatitis requires the use of immunostimulants. Drugs to upsurge the movement of the body’s fortifications. If the cause is not an infectious factor, but an autoimmune process, allergy – hormonal agents and antihistamines are indicated. With this type of disorder, it is important to prevent relapses. So that remission lasts as long as possible. It is problematic to completely cure chronic forms of stomatitis.
Prognosis and prevention of the disease
In most cases, aphthous stomatitis has a favorable prognosis. With timely treatment, ulcers heal within 7-14 days without scarring (except for severe forms). However, with a chronic recurrent course, frequent exacerbations are possible. They are painful and seriously decrease the superiority of life.
Prevention is usually not difficult. It is enough to follow a number of measures:
- stick to proper oral hygiene.
- avoid injury to the mucous membrane;
- support the immune system: the right food, suitable amounts of vitamins and rest.
- exclude from your diet foods that provoke allergies (citrus fruits, chocolate, spices);
- treat chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine and immune systems;
- avoid stress, normalize your emotional state if possible.
- Deal with infectious diseases and caries in a timely way.
It is also important to give up cigarettes and not abuse alcohol. If characteristic symptoms develop, you should contact a general dentist. He will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.