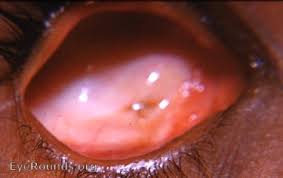
Anophthalmos is an ophthalmopathology characterized by the absence of the eyeball in the orbit. Clinical manifestations of the disease are irreversible loss of visual functions on the affected side, narrowing of the visual field, impaired spatial perception and rapid fatigue when performing visual work with the healthy eye. Diagnostics include external examination, biomicroscopy of the eye, ultrasound and pathomorphological examination. Specific treatment is based on step-by-step prosthetics. Instillations of antiseptic agents are additionally indicated. Surgical correction of cosmetic defects is performed according to individual indications.

General information
Anophthalmos is a common ophthalmopathology. According to statistics, the prevalence of the congenital form is 1-2.1 per 10 thousand of the population. In adulthood, this figure fluctuates between 21 and 22.3 per 10 thousand, since about 12,000 enucleations are performed on patients each year. In pediatric patients, the disease is spotted in 0.5% of cases. Removal of the eyeball is a forced measure in 5-12% of patients with a history of severe eye trauma . Today, the number of patients living in Russia and requiring ocular prosthetics has increased to 300 thousand people.
Causes of anophthalmos
Anophthalmos is classified as a polyetiological disease. The trigger factor for the development of the congenital form cannot be accurately determined in most cases. The main causes of congenital and acquired forms of pathology are considered to be:
- Intrauterine infections . Anophthalmic syndrome may be a consequence of the action of measles , rubella or herpes zoster viruses at the stage of embryogenesis.
- Amniotic bands . Amniotic crowd disease remains the cause of multiple pathologies of the visual organ. Depending on the gestational period at which they were formed, anophthalmos or milder forms of eye damage ( hypertelorism , strabismus , microphthalmos , glaucoma) develop.
- Genetic syndromes . Anophthalmos often occurs in combination with multiple developmental anomalies against the background of chromosomal pathologies ( Patau , Lenz, Lochmann syndromes) or mutations of the PAX6, SOX2, OTX2 and VSX2 genes.
- Action of teratogenic factors . Ionizing radiation, consumption of alcoholic beverages, some pharmacological preparations, and narcotic drugs have a teratogenic effect on the organ of vision.
- Traumatic injuries . Anophthalmos may develop as a result of domestic or industrial injuries. Enucleation is used due to the occurrence of post-traumatic atrophy, chronic uveitis or a high risk of sympathetic ophthalmia .
- Oncological diseases . Elimination of the watch container be achieved in the presence of a malignant tumor.
Pathogenesis Congenital anomaly of the eyeball development occurs under the influence of teratogenic factors in the 2nd-6th week of embryogenesis. During this period of time, the process of laying down the organ of vision is disrupted. Through a flaw in the assembly of the essentials, the course of development of the optic vesicle and the aforementioned further changeover to the optic cup is terrible.
If the influence of pathogenic factors falls on the moment of the already formed optic cup, then its low-differentiated rudiment can be found in the orbital cavity. Anophthalmos can be an early manifestation of a genetic syndrome caused by a gene or chromosomal mutation. Acquired pathology develops as a result of massive damage or surgical removal of the eyeball.
Classification
By the time of occurrence, anophthalmos is classified as congenital and acquired. A unilateral or bilateral variant is possible. This type of systematization is used at the stage of diagnosis. From a clinical point of view, the following forms of pathology are distinguished in practical ophthalmology :
- True . The disease is combined with the absence of the lateral geniculate body, chiasm, optic nerve and its canal. The true type is exclusively congenital and often occurs simultaneously with other developmental defects like myopia .
- Imaginary . A whole lack of the sense is open. Other orbital structures are characterized by a normal anatomical and physiological structure. Radiographic diagnostic methods allow visualization of the optic nerve canal.

Symptoms of anophthalmos
Anophthalmos remains displayed by irreparable damage of filmic jobs. In the unilateral form of the disease, the visual acuity of the other eye may correspond to the norm. The loss of binocular vision leads to a narrowing of the boundaries of the visual fields, a violation of spatial perception. Patients present asthenopic complaints associated with rapid fatigue of the accommodative apparatus. Adaptation to monocular depth vision occurs better at a young age. When enucleation is carried out due to blindness , adaptation occurs as visual dysfunction progresses. The combination of anophthalmos with damage to the nervous system leads to severe pain in the projection zone of the orbit with irradiation to the back of the head.
Complications
The absence of timely step-by-step prosthetics in the congenital form of anophthalmos leads to facial asymmetry . On the affected side, there is a drooping eyebrow, raised wing of the nose and corner of the mouth. As the child grows, the severity of the deformation increases, which entails a violation of the respiratory function and the act of chewing. The presence of a low-differentiation rudiment of the eyeball in the orbital cavity is often the cause of complications of an infectious and inflammatory nature. In some cases, a retrobulbar abscess or orbital phlegmon develops .
Diagnostics
Visually, the absence of the eye in the detour hole is resolute. The shape of the conjunctival cavity is close to conical, reduced in size. Narrowing of the palpebral fissure is combined with internal epicanthus, entropion or complete absence of the fold of the upper eyelid. Instrumental diagnostics include:
CT of the brain . CT is used for differential diagnostics between imaginary and true forms of anophthalmos and microphthalmos. In the imaginary form, the optic nerve canal is visualized. A individual feature of microphthalmos is the occurrence of a ailing discerned seed in the detour cavity.
Biomicroscopy of the eye . The study allows us to identify disproportionality of the conjunctival fornices, a narrowed palpebral fissure, incorrect position of the eyelids, multiple scars and adhesions.
- Ultrasound of the eye . The use of the technique is recommended for assessing the condition of the orbital cavity, determining the echogenicity of the contents of the orbit.
- Pathomorphological examination . The method enables the ophthalmologist to establish the degree of eye reduction and its correlation with the stage of embryogenesis.
All patients with the congenital form of the disease are recommended to consult a geneticist, since anophthalmos can be an early manifestation of genetic pathology. The addition of neurological symptoms, pain and facial asymmetry require examination by a neurologist.
Treatment of anophthalmos
It is impossible to restore visual acuity in anophthalmos. The area of action is to remove the cosmetic flaw and avert problems. Surgical tactics come down to step-by-step prosthetics, which must be performed in early childhood with a gradual replacement with a larger diameter prosthesis. Eye prosthetics are did in some stages:
- Preparation . Radical intervention is indicated – enucleation or removal of the rudiment of the optic cup. In case of a pronounced defect of the orbital walls, their surgical plastic surgery is performed.
- Individual prosthetics . Development of a prosthesis taking into account the color blindness and relief characteristics suitable for the patient.
Conservative therapy for anophthalmos is reduced to daily instillations of antiseptic solutions. In case of severe eyelid defects, surgical correction of lagophthalmos and entropion is performed. Canthotomy is justified only after the patient reaches 18 years of age, since earlier intervention is complicated by entropion.
Prediction and prevention
The principle of step-by-step prosthetics in the treatment of patients with anophthalmia allows eliminating cosmetic defects and preventing the formation of bone deformations of the facial part of the skull. It is impossible to restore visual functions with this pathology, but the disease does not pose a threat to the patient’s life. Specific preventive measures have not been developed. Non-specific prevention of the acquired form is reduced to compliance with safety precautions at work and at home. To reduce the jeopardy of emergent inborn astigmatism. It is necessary to circumvent the teratogenic properties of various features from the 2nd to the 6th week of gravidness.