Adentia

Adentia is a pathological condition in which a person is missing one tooth, several teeth, or many teeth in a row. The complaint happens in patients of all ages. It occurs in both children and adults. Moreover, with age, the prevalence and severity of the pathological condition gradually increases for obvious reasons. Natural wear and tear, demineralization of units, destruction due to caries, etc. are observed. Adentia creates many problems. From improper distribution of the load on the entire dental row to inflammatory processes in the joints, as well as early loss of other teeth. It is definitely not worth leaving the disorder unattended: the loss of even one unit is fraught with very serious problems.
Treatment of changes is carried out by doctors of several specialties: dentists-therapists , implantologists, orthopedists and others.
Causes of adentia
Adentia develops for various reasons. They can be congenital or acquired. The problem is very widespread. According to our statistical estimates and studies, the pathological condition develops in almost 25% of people under 40 and in almost 70% of people over 60. Moreover, it is often not the absence of one tooth, but the loss of several units. By the age of 80, complete adentia often occurs, which is accompanied by the absence of teeth on the upper and lower jaws.
The problem is much less common in children (changing teeth from baby to permanent ones is not considered adentia, at least most specialists agree on this position). Usually the causes are congenital, hereditary or spontaneous. In all cases, an assessment of the causes of the disorder is required. The effectiveness of the treatment of the disease depends on understanding the essence of the phenomenon (relatively speaking, adentia is more of a pathological condition than a disease).
Those who experienced and participated in the violation
When talking about the culprits of the pathological process, it is necessary to distinguish between the causes of primary and secondary damage to the dentition.
Primary damage is congenital. We are talking about the absence of a rudiment of a milk tooth and gum . Therefore, it simply does not erupt.
Hereditary arrangements of the unreasonable progression are very, very intermittent. According to various sources, they occur in no more than 0.8-1.1% of cases of the total number of forms of adentia. But the probability of the disorder should not be written off.
Children who have encountered the absence of a milk tooth rudiment often also lack rudiments of a permanent unit. And then the disorder passes from early to mature age and still requires correction. Other prosthetics, including implants. Decisions on therapy will be made based on the patient’s condition and what the patient wishes.
Acquired forms of adentia constitute the bulk of clinical cases. The pathological condition is always based on certain processes, changes that affect the condition of individual teeth and the entire human dental system. There are many reasons. Most often, the development of adentia occurs due to:
- caries, a destructive process in the tooth area, the disorder develops gradually, without treatment it leads to the loss of a unit, but with the right approach this dental disease can be effectively treated;
- pulpitis, as a complication of caries, inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of the tooth is formed, when it dies, the unit becomes much less viable, since both the blood supply and local protection are lost;
- periodontitis, an inflammatory process in the area of tissues that hold the tooth in a normal anatomical position, the disorder is progressive in nature and therefore requires the earliest possible correction;
- periodontosis, a dystrophic process in the periodontal area, often with an inflammatory component, no less dangerous than periodontitis;
- periodontitis is an inflammation of the dental ligament, deep tissues near the root that hold the tooth, as a rule, periodontitis in a patient develops with a long course of pulpitis caries, as a complication;
- injuries, damage often occurs in children and young people, in some cases the tooth can be returned to its place and restored, in others – not, sometimes an entire segment of the dental row is affected (for example, with a jaw fracture).
A rare, but still possible condition is the resorption or other damage to the rudiment of a permanent tooth. Unlike the congenital form of adentia, when there is no rudiment at all, it is acquired. The rudiment can be resorbed for a variety of reasons. In some children, resorption occurs after a facial injury. In others, it is a consequence of severe caries in baby teeth (damage to the rudiment is often observed, especially with an aggressive course of the pathological process in the patient). The death of the rudiment also develops with other pathologies of the oral cavity. Autoimmune factors are possible, but they have been studied much less.
According to our estimates, resorption of the rudiment is observed in 5-7% of children without caries or with a moderate course of the disease and in almost 15% of children who face early and aggressive tooth decay. As a rule, 1-3 units are missing. It is impossible to radically change this situation. It can only be prevented. The treatment is orthopedic.
Dentist-therapist
Assessing the cause of the pathological condition is the job of a specialist doctor. A full dental examination is indicated. Instrumental studies are also carried out (targeted, survey radiography, etc.).
Pathogenesis of adentia

The pathogenesis of the absence of one or a row of several teeth varies from case to case.
If we talk about primary damage, a congenital disorder, it can be the result of:
- the influence of toxic factors on the mother’s body;
- a consequence of an immune conflict between the mother and fetus (most often observed when the child has a positive Rh factor and the mother has a negative one);
- the result of genetic abnormalities and diseases, in which case adentia is just one of the disorders in a wide range of pathological changes, often observed underdevelopment of the lens, joint pathologies and much more.
Acquired forms are caused by completely different pathogenetic factors and mechanisms:
- inflammatory processes in the area of the tooth structure (then there is a risk of resorption of the rudiment in a child or loss of a tooth in patients of all ages);
- toxic, chemical effects on tooth structures;
- traumatic bearing on the indentation.
In each case, the mechanism is different. But the outcome is the same – the loss of one or several units. And such a condition in all cases requires correction. As quickly as possible. Simply because complications develop quickly, which affect the function of the entire dental system and not only.
Risk factors for developing the problem
Adentia as the absence of teeth develops for the reasons described. However, the problem has a broader context. Even with the presence of characteristic problems, the development of pathology is not observed in everyone. This happens due to risk factors. If they are present, the probability of adentia is higher. Among them:
- hormonal imbalances of a natural nature (especially often observed in women);
- pregnancy, since nutrients are spent on the development of the fetus, demineralization of enamel occurs, teeth become much more sensitive to negative factors;
- diabetes mellitus, especially in its decompensated form, when the patient does not control the blood sugar level (with compensation for the disorder, the risks are no higher than those of the average, conditionally healthy person);
- other systemic diseases;
- poor nutrition, an abundance of fast carbohydrates, since they are an ideal nutrient medium for the flora of the oral cavity;
- inflammatory processes in the oral cavity;
- smoking, active consumption of nicotine is a factor in the development of tartar and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity;
- consumption of alcohol and drugs.
There are also other risk factors, no less dangerous. They need to be fought and can be fought. Under the supervision of a doctor or on your own. Depending on the situation.
Types, classification of adentia
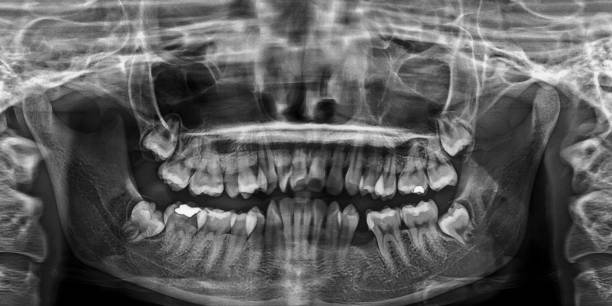
The classification of the pathological condition is carried out on various grounds. congenital;
- acquired.
Congenital forms are observed from birth. They are rare. Acquired, as was said, are the result of human life activity. Adentia of this kind can develop at any time. But it prevails in old age.
The same classification often suggests other names. Adentia can be primary or secondary. Primary is congenital, secondary is acquired.
Depending on the prevalence of the defect, adentia can be:
- complete;
- incomplete or partial.
Complete adentia is a condition in which the tooth is completely missing Partial is classified in even more detail. The defect can be:
- small, when one tooth is missing;
- average, when there are not 2-3 units;
- extended or severe, when there are no more than 3 teeth in a row.
The arrangement of handy modules of adentia affording to Kennedy is broadly used. It is based not so much on the extent of the defect, but on the potential possibility of a particular treatment. Accordingly, adentia is distinguished:
- Class 1, when there are no chewing teeth on both sides of the jaw;
- Class 2, when there are no chewing or other teeth on one side;
- Class 3, in this case the defect is on one side, but some of the chewing teeth are preserved, this condition is considered less severe, since there is the possibility of treatment with a larger number of methods (installation of bridges, etc.);
- Class 4, when there are no teeth in the smile zone (frontal area: incisors, canines).
Please note!
All the described classifications are actively used to describe the essence of the pathological process. They have not only a theoretical but also a practical purpose. This is important for the prompt determination of the most suitable and high-quality method of treatment, prosthetics.
Associated symptoms of pathology
The main symptom of adentia is the absence of one or many, all teeth. However, this condition has many more manifestations. Among them:
- formation of deep nasolabial folds, wrinkles;
- changes in the contour of the face, resulting in visual aging of 5-10 years, depending on where the defect is located, how extensive it is, the presence or absence of concomitant pathologies of the patient’s dental system;
- possible deformation of the facial skeleton, which is manifested by facial asymmetry;
- changes in diction, some sounds become difficult to pronounce;
- cosmetic defect, if there are no teeth in the frontal area, it will be clearly visible.
The symptoms are eliminated in one accessible way – through treatment. If one tooth &many teeth are lost – prosthetics are indicated. And as soon as possible. Since the likelihood of complications increases every day. Many are unnoticeable and manifest themselves at the moment when the patient decides to restore the dental row, its integrity.
Complications of the pathological condition
The disorder has a lot of complications. The more severe the pathology, the more difficult the situation.
Inevitably, bone loss and alveolar process atrophy develop. Jawbone material entertainments as a sustenance for grafts. Therefore, it may happen that the patient will face the impossibility of implantation.
Important!
Of course, this is not a reason to refuse prosthetics on implants. It will just require more preparation. The so-called bone grafting or osteoplasty is performed. Or there are protocols that allow implantation without preliminary surgical treatment. But they are initially somewhat more expensive than their analogues.
Bone loss, and noticeable loss, begins within 1-2 months after tooth loss. So you need to act quickly.
Cosmetic problems often develop. Aging, changes in facial contours, the appearance of wrinkles. These are reversible changes, but they can provoke psychological discomfort.
Teeth become mobile. The fangs are nearby the fault move near the free space. As a result, severe bite disorders develop. Therefore, defects need to be treated in a timely manner.
There are problems with diction and digestion. The nonappearance of even one prong makes the courses of talking and eating challenging.
The load on the dental row is distributed unevenly. As a result, the remaining teeth wear out much faster than they should. In addition, the likelihood of inflammatory and degenerative processes in the temporomandibular joint (abbreviated TMJ) increases. Arthritis and arthrosis are possible.
The only preventive measure for complications is to resort to orthopedic dentistry methods. Correction of adentia. And the sooner the better.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of jaw adentia does not present significant difficulties. They are obvious. To establish a diagnosis and determine the nature of the pathological process, a group of measures is indicated:
- oral questioning of the patient to assess complaints;
- collecting anamnesis to more accurately understand the origin of the defect of the upper or lower jaw;
- visual assessment of the oral cavity condition, carried out to confirm the defect, assess its location and severity (primarily).
This is enough to make a characteristic diagnosis. But it is not enough: it is much more important to develop correction measures. And this can only be done by conducting an additional examination. You would need:
- overview radiography of the dental system and dentition (orthopantomography);
- targeted X-rays of the area where the defect is formed;
- CT with construction of a three-dimensional model of the dental system and assessment of the thickness and density of bone tissue.
The point is not only to diagnose adentia, but also to evaluate the individual parameters of the clinical case. This is the minimum program of the necessary research. analysis of hereditary, genetic predisposition, karyotyping under the supervision of a geneticist (to identify congenital types of pathological processes);
Evaluating hormone levels to look for a relationship between endocrine disease and dental abnormalities.
And so on. The list of studies remains at the discretion of the doctor.
Treatment of adentia
Treatment of adentia consists of restoring the dental row. The result can be achieved only by prosthetics. This is not one method, but a whole group of measures of various nature.
There are removable options. Changeable dentures for edentia can be uninvolved self-sufficiently, lacking the sharing of a medic. This category includes complete removable dentures (plate, acrylic, nylon or Acry-Free), immediate dentures, and others.
Conditionally removable dentures allow you to replace several teeth. Basically, we are talking about clasp structures (on a metal base or on a plastic base – the so-called Quadrotti). Even though they’re costly, they will last longer and work more reliably. The process of choice was and still is mainly implantation. Dental inserts are untruthful titanium poles positioned into your jawbones. They performance as new origins in the organization. Artificial crowns are fitted over the implant when they are installed. Your teeth exertion to figure your food and assistance you chew it too. Safety is a defining feature of the installation. Still, great care is needed by skilled doctors, quality instruments and proper planning.
Modern methods allow you to achieve results immediately. There are different protocols, that is, methods of implantation:
- classic – installation of each tooth on its own implant, the titanium support needs to take root (4-6 months), only then a crown and prosthesis are installed, until then the patient uses temporary structures;
- basal, installation of 8-10 implant-screws, but at a greater depth (into the basal layer of the bone), they are fixed more securely from the very beginning, the load is immediate, in other words, a functional temporary prosthesis is immediately installed, which replaces the lost teeth, there is no need to wait for osseointegration, engraftment;
- All-on-4, 6, both methods are used in case of loss of all teeth, complete edentia, allow to restore the dental row even with bone tissue atrophy without preliminary preparation.
All treatment decisions are made by orthopedic dentists and implantologists. In agreement with the person. Specialists offer available options and describe each one. Its advantages and disadvantages.
Prognosis and prevention of adentia
The prognosis for adentia without treatment is always unfavorable. The probability of complications is constantly increasing, then more and more consequences of adentia develop. With appropriate treatment – always favorable. Since negative consequences always occur, in case of tooth loss it is strongly recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Prevention is simple and universal – you need to take care of your teeth:
- follow hygiene rules used a toothbrush and dental floss;
- prevent the development of injuries;
- undergoes hygienic cleaning at a dental clinic every year; professional hygiene helps to avoid the development of caries;
- eat rationally and qualitatively;
- give up cigarettes and alcohol.
Prevention of adentia is not difficult. But it requires discipline. If the problem develops, a doctor’s consultation is recommended.
Answers to questions
What to do if one tooth is missing?
If one tooth is missing, you can install a removable, clasp denture or undergo a classic implantation procedure. Implantation in this case is the most preferable option in all respects.
Is it possible to undergo implantation at a young age?
You can undergo implantation at any age, if your health allows it and there are no contraindications. Normally talking, the subordinate limit is 19 years. Simply because the dental system is still developing.
What to do if the bone starts to shrink?
When bone loss develops, osteoplasty is needed. Bone grafting allows restoring normal bone volume. In some belongings, it is thinkable to resort to implantation protocols that do not require osteoplasty . But here, too, there may be some nuances. Implantation for edentia is performed on an individual basis.
Which method of prosthetics is the best, which one to choose?
The choice of prosthetic method depends on the specific situation. There is no concept of the best method for restoring a dental row. The issue is resolved individually in all cases. The best method can only be discussed within a specific case, and not in general. However, the most durable, aesthetic method of correction was and remains implantation.
