Alveolitis
Alveolitis is an serious seditious development in the zone of the tooth opening. It usually develops after the extraction of a tooth, as a complication of surgical intervention. Much more often it develops during the so-called complex extraction, when tissue trauma is quite high. The disease (although formally it is not a disease, but a pathological condition) develops in a significant proportion of patients after extraction.
The disorder has other names, such as dry socket syndrome, which reflects the absence of a blood clot, which should normally be at the bottom of the socket after extraction. The disease is also called alveolar osteitis. The disorder is characterized by a fairly mild course. However, it can provoke complications, although this is not so likely. Diagnosis and treatment of the pathological condition is carried out by a dentist . Antiseptic treatment of tissues is carried out.
Causes of alveolitis
Alveolitis is based on an acute inflammatory process that affects all tissues of the alveolar socket. The place where the tooth is normally fixed. Inflammation occurs suddenly. Usually on the few day after the process. But there are many known cases when the disorder developed in a matter of hours or later. About a week later. Therefore, near is no need to talk about severe goals.
According to statistics, alveolitis develops in 3-6% of clinical cases on average. When removing a wisdom tooth, the probability of an inflammatory process is much higher and is about 40%. Other factors. No one is immune from complications. According to our estimates, the pathological condition develops in adults and children equally often. But there are some additional patterns. Thus, women experience alveolitis almost 5 times more often than men.
Apparently, this is due to the specifics of the hormonal background and its influence on the processes of natural tissue healing. When removing lower teeth, the probability of a pathological process is higher than when extracting upper teeth. Finally, teeth with a large number of roots are more difficult to remove and give complications much more often. This may caues of caries. Doctors take these factors into account when planning surgical treatment.
The immediate cause of the development of the pathological process, alveolitis, is tissue trauma. It is higher when affecting teeth with a large number of roots, a complex fixation system. The inflammatory phenomenon has its own pattern of development, pathogenesis and increased risk factor
Pathogenesis of the disorder
The pathogenesis of alveolitis is based on a group of mechanisms or factors.
First, the alveolar socket is traumatized. It is inevitable when removing any tooth. The only question is the degree of trauma. The more experienced the doctor, the lower the probability of serious tissue damage. The integrity of the vessels, periodontium, and periodontium is violated. If the extraction is carried out using complex methods (the tooth has many roots, it is impacted, etc.), the degree of trauma will initially be significantly higher.
Immediately after tooth extraction, a blood clot forms. This is a kind of natural barrier between the socket (bone tissue) and the external environment. The blood clot plays a major role in addition to this. It itself is compacted by fibrin. In the process of natural blood clotting. Then it is covered with granulation tissue. Young epithelial cells that will form the future surface of the healed wound surface. Also, vessels grow through the clot, which are responsible for the restoration of local blood flow, and therefore the activation of healing processes. With alveolitis, the course of clot development is disturbed:
- it is absent altogether, this is the most severe option;
- breaks down too quickly;
- It does not have a dense texture, instead the structure is loose, which is why healing occurs much slower than under normal conditions.
Due to the absence of a blood clot, the tooth socket tissue communicates with the oral cavity and the external environment in general. As a result, pathogenic and opportunistic flora, fracture tooth
, penetrates the wound. Irritation matures as a answer to bacteriological or mycological, viral tissue damage. The addition of a purulent component is possible. This is fraught with serious complications that will require serious assistance. It is quite possible that in this case the patient will have to be treated in a hospital, surgically.
With correct verbal cleanliness and excellence care. The probability of commotion of the remedial process is minimal. If the disruption has begun, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible. Preferably on the day of the development of pain and other symptoms of alveolitis.
Risk factors for the development of pathological process
Alveolitis does not develop in all patients who have had a wisdom tooth or other tooth removed. This happens because of the difference in anamnesis. The probability of a pathological process is higher in the presence of so-called risk factors. There are many of them. Among them are:
- insufficient qualification of the doctor, tooth extraction is a complex process, the probability of illness depends on the degree of trauma of the treatment, the more experienced the doctor, the more accurate the final result;
- general complexity of removal, extraction of a tooth from the alveolus is a difficult process if the tooth has many roots, it has partially erupted, or is displaced from its normal position – this creates additional risks;
- location of the problem tooth in the lower jaw;
- the need to remove molars; multi-rooted teeth are generally more complex in terms of consequences and removal technique than teeth with one root (incisors, canines and in some cases premolars);
- the presence of systemic diseases in the anamnesis, the probability of a pathological process is significantly higher if a person has chronic diseases, especially blood clotting disorders, diabetes mellitus and other disorders that affect tissue regeneration processes;
- Nicotine consumption increases the likelihood of alveolitis many times over;
- oral infections, dental and gum diseases, as an increased infectious load develops;
- alcohol consumption, due to a decrease in local immunity, complex disruption of the body’s defenses;
- poor oral hygiene, disruption of the formation of a blood clot in the wound area due to aggressive cleaning, attempts to touch the socket with the tongue, etc.;
- the introduction of a large amount of anesthetic drug, modern anesthetics contain adrenaline, it constricts blood vessels, which prevents active bleeding, but at the same time causes ischemic processes, fraught with inflammation after the treatment;
- elderly and senile age of the patient, the older the person, the higher the likelihood of acute inflammation of the socket and other problems;
- acute inflammatory process in the oral cavity.
- Many of these risk factors are highly modifiable and mitigable. Careful preparation is highly recommended before tooth extraction.
- Symptoms of alveolitis
- Dry socket or alveolitis has a somewhat exact medical picture. The symptoms of the pathological process are as follows:
- pain;
- feeling of discomfort in the area of surgery;
- bad breath;
- Bruxim
- visual changes.
- Toothache develops very often. It is the main and often leading manifestation in the clinic of the disorder. It develops several hours or days after the intervention. Therefore, it is necessary to pay maximum attention to your own condition. The pain is shooting, aching or pressing. It intensifies when touching the tissues, eating, and performing oral hygiene. As the acute inflammatory process progresses, the pain becomes stronger. It radiates to the temple, jaw, facial area and even the head (due to the proximity of the trigeminal nerve, which has a complex branching).
The feeling of discomfort is not pain. Patients describe the unpleasant sensations associated with alveolitis very differently. Some talk about pressure, others about distension. Some complain of itching, burning in the problem area or numbness. Each case has its own symptoms.
Bad breath is often the result of active accumulation of food debris in the tooth socket area. This is especially common with poor hygiene after surgery or deep tissue trauma. The pathological condition is accompanied not only by bad breath, but also by a feeling of an unpleasant taste. In severe cases, pus may flow. This is a clear sign of secondary bacterial inflammation.
Visual changes are characterized by gaping of the tooth socket. No traces of blood are visible. The bone is visible, covered with a yellowish, grayish or beige coating.
Important!
The manifestations of the pathological process are specific. But in some cases they can mask other, equally or more dangerous pathological conditions. For example, gumboil, an inflammatory process in the periodontal area or something else. It is not customary to diagnose alveolitis by eye. A thorough diagnosis is indicated.
Symptoms of general intoxication of the body may develop. Increased body temperature, weakness, drowsiness, feeling of general malaise. These are strong symbols of the connection of the full body in the course. But not always a sign of the severity of the pathological process. Everything is individual.
Complications of alveolitis

The issue of complications of the pathological process remains controversial. Some authors point out that alveolitis, although it provokes a lot of discomfort, does not pose a great danger and responds well to therapy. It can also regress on its own after a certain time (though longer than with quality treatment). Yet, not everyone decides with this position. The literature describes enough cases of various complications:
- osteomyelitis, this is an inflammatory process on the part of the bone, it is serous or purulent in nature, fraught with not only the loss of teeth, but also the destruction of the jaw bone, the development of soft tissue damage and more;
- phlegmon, an inflammatory process of the soft tissues, subcutaneous fat of the face and neck, an extremely dangerous condition and requires urgent treatment under the supervision of specialists, including surgery, since a fatal outcome is possible;
- odontogenic sinusitis or, more only, an seditious procedure of the maxillary sinuses from the adjacent of the conduct accepted out, can be a significance of the withdrawal of a tooth on the greater jaw, due to the structural proximity of the sinus;
- lymphadenitis or lymphadenopathy, inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes due to the penetration of an infectious agent, most often bacteria;
- development of an abscess, which risks developing into phlegmon;
- Sepsis otherwise known as blood poisoning develops with the intensive spread of bacteria throughout the body & is prevalent in patients with weakened immunity, HIV and other deficiency conditions of various kinds.
In less severe cases, widespread periodontitis of adjacent teeth may develop. If alveolitis is not treated, a person risks losing adjacent teeth. Complex and fairly long-term treatment under the supervision of specialists will be required. In addition, it is expensive. It is much easier to cope with alveolitis at the very beginning than to eliminate secondary disorders.
Diagnosis of alveolitis
Diagnosis of the pathological process does not present any significant difficulties. A group of methods is used to identify the pathological process:
- an oral survey is carried out to determine the symptoms of the pathological process, all complaints and manifestations are carefully recorded, signs of alveolitis after tooth extraction are quite characteristic, especially if a full range of studies is carried out;
- anamnesis collection is carried out to assess the probable origin of the disorder; alveolitis in all cases is associated with the extraction of the patient’s tooth, which means that it is easy to link what happened and the symptoms and health complaints that developed;
- examination of the oral hollow. Which contains a systematic investigation of the complaint of the oral cavity & dentition and adjacent tissues is compulsory
- overview radiography or orthopantomogram, which is performed to assess the condition of the tissues of the dental system;
- A targeted image, to determine and understand the structure of the tissues around the alveolar socket, its condition, first of all gives an idea of the condition of the bone.
Sometimes tests are performed to assess the severity of the inflammatory process in the patient. The exact list of necessary studies is determined by a medical specialist.
Treatment of alveolitis
Treatment of the pathological process is carried out under the supervision of the doctor who performed the removal or another specialist. Correction is usually quite simple. The basis is drug treatment.
Antiseptic treatment of the alveolar socket is carried out using special mild preparations. Duration and frequency of use are individual matters. The doctor decides on this, taking into account the severity of the clinical case. Anti-inflammatory drugs are used. They are needed to alleviate the symptoms of inflammation, as well as to relieve pain symptoms. Healing preparations are actively used for treatment and care.
Please note!
As a rule, handling is supported out on an casualty origin. At home, without placing the patient in a specialized maxillofacial hospital. But if the patient has purulent inflammation of the socket, symptoms of general intoxication of the body, severe malaise, there is a risk of complications – careful treatment in the hospital is indicated. Dental department. Including the use of antibiotics, if the inflammatory process is caused by microorganisms, pathogenic or opportunistic flora, and not viruses or fungal agents.
Prognosis and prevention of alveolitis
Alveolitis after tooth extraction is a widespread phenomenon. It transpires in a momentous sum of patients. In some cases, the disorder regresses on its own. But in this case, there are risks of developing secondary disorders. They become a consequence of acute inflammation. Alveolitis is treated well, the risk of negative consequences can be eliminated almost to zero. Therefore, the prognosis is generally always positive.
As for prevention, it is simple and does not require serious efforts. Although there is no specialized prevention program. Among the measures:
- Quitting cigarettes and alcohol, substance abuse provokes alveolitis most often;
- a competent choice of a medical specialist with sufficient experience, skills and knowledge;
- strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations after tooth extraction;
- careful but thorough oral hygiene, do not use a toothbrush to clean the affected area, special antiseptic rinses are recommended, etc.;
- careful consumption of food, avoiding hard, sticky and other similar foods.
You must not dash the plasma accumulation with your language, so as not to injury it. If symptoms of the inflammatory process develop, you need to see a doctor. If the symptoms intensify, too. Since it is possible to transition to more dangerous forms of pathology. It is best to treat tooth alveolitis at the very beginning of the disorder.
Can alveolitis go away on its own?
It can. And the probability of an enamel hypopliasia outcome is quite high. But there are two problems here. The first is a significant level of distress which lessens the quality of life. The second is the risk of complications. Therefore, it is better not to wait, but to contact a specialist doctor. This is the optimal strategy in terms of the probability of high-quality recovery without the risks of a negative scenario.
How long does it take to treat alveolitis?
How long to treat alveolitis is an individual matter. In mild forms of the inflammatory process, when they were detected at the initial stage, when there is no purulent component, 3-5 days are enough. In other cases, a little more time is required.
Is surgery necessary?
If the case of alveolitis, tooth socket damage is not advanced – no. Surgical treatment of the pathological process is not required. The condition is normalized with conservative correction of the pathological process. Antiseptic treatment & high quality care and the use of anti inflammatory drugs are sufficient.
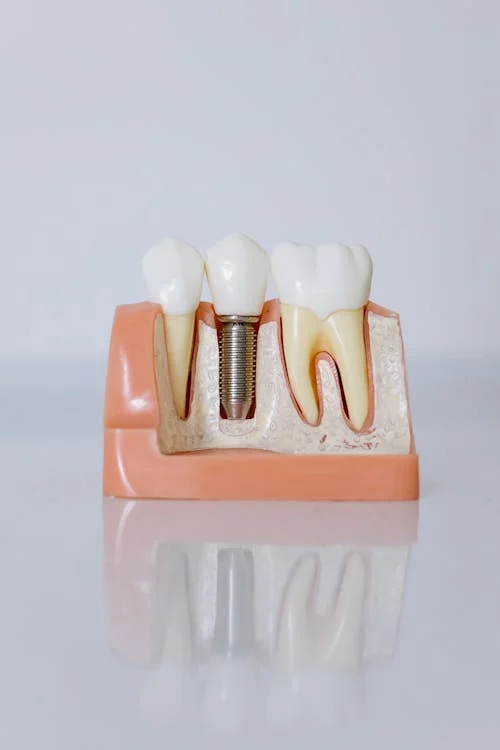
Is it possible to implant teeth after alveolitis?
Yes, it is possible. But first, the inflammatory process must be completely cured. Implantation is possible only after high-quality treatment of alveolitis. Not earlier.
