Adenoviral conjunctivitis ( Pharyngo-conjunctival fever )
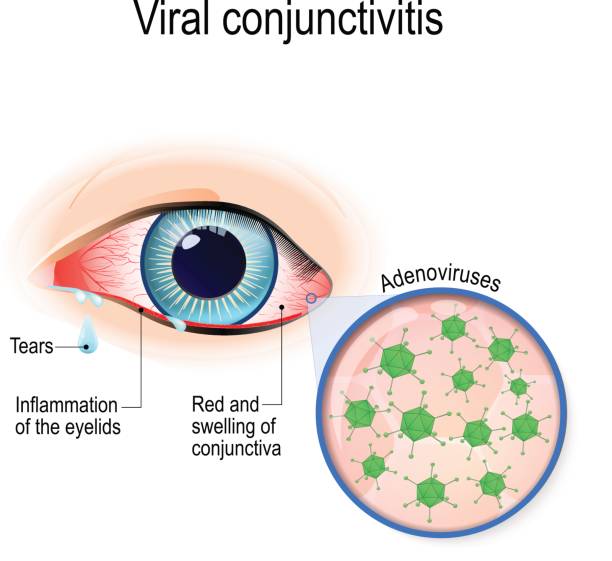
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is an acute infectious lesion of the mucous membrane of the eye caused by adenoviruses. Adenoviral conjunctivitis is accompanied by fever, nasopharyngitis, local symptoms (swelling of the eyelids, hyperemia of the mucous membrane, lacrimation, burning, pain, itching, discharge from the eyes). Diagnosis of adenoviral conjunctivitis is performed by an ophthalmologist taking into account the data of a bacteriological examination of a smear from the conjunctiva and a PCR scraping. Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis includes instillation of antiviral and antibacterial drugs, application of eye ointments.
General information
Adenoviral conjunctivitis (pharyngoconjunctival fever) is a highly contagious infection caused by adenoviruses and occurring with inflammatory lesions of the conjunctiva, the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract (pharyngitis), an increase in body temperature. In
ophthalmology
Epidemic outbreaks of adenoviral conjunctivitis are usually recorded in the autumn-spring period, mainly in organized children’s groups.
Reasons
The instrumental managers of adenoviral conjunctivitis through wide-ranging occurrences are adenoviruses of serotypes 3, 7a, 11; in sporadic cases – adenoviruses of types 4, 6, 7, 10. Adenovirus gets on the mucous membrane of the eye when sneezing, coughing or directly introducing the infection from contaminated hands. From the moment of infection to the appearance of clinical symptoms, it takes from 3 to 10 days (on average 5-7 days). High-risk factors are:
- contact with a patient with adenoviral conjunctivitis;
- hypothermia , acute respiratory viral infection ;
- violation of hygiene;
- swimming in polluted bodies of water and pools;
- eye injuries ;
- failure to comply with the rules for wearing and caring for contact lenses;
- surgical treatment of corneal pathology;
- stress.
Pathological anatomy
Cytological examination of smears in patients with adenoviral conjunctivitis reveals destruction of epithelial cells, characterized by vacuolization, chromatin breakdown, hypertrophy of nucleoli, and formation of a nuclear membrane. Mononuclear cells predominate in the cytogram.
Symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis
According to the clinical course, catarrhal, follicular and membranous forms of adenoviral conjunctivitis are distinguished. Catarrhal and follicular adenoviral conjunctivitis can occur at different ages, membranous develops mainly in children. The clinical picture manifests itself 5-8 days after infection. At the beginning of the disease, an increase in body temperature with pronounced pharyngitis and rhinitis , headache , dyspeptic disorders are noted ; submandibular lymphadenitis develops .
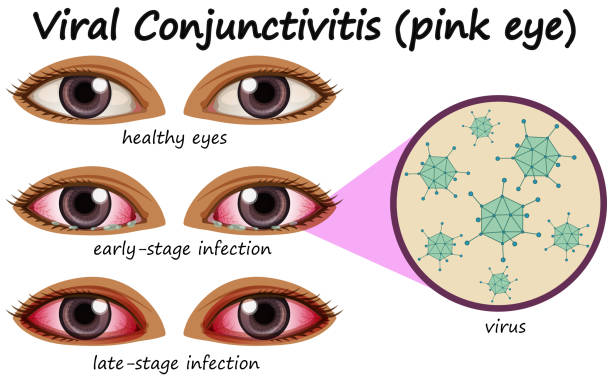
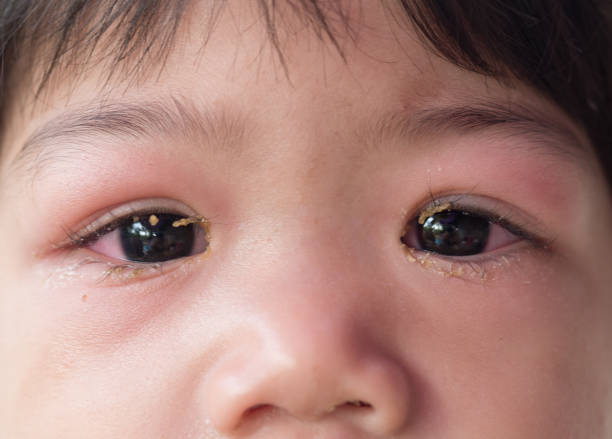
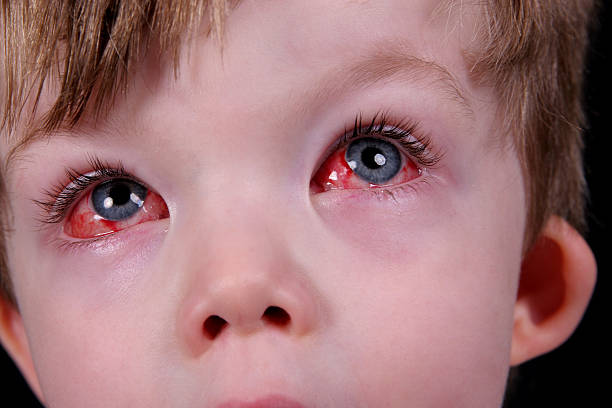
During the second wave of fever, signs of conjunctivitis appear first in the area of one eye, and after 2-3 days – in the other eye. Local symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis are characterized by swelling and redness of the eyelids, scant mucous or mucopurulent discharge, a sensation of a foreign body , itching and burning, lacrimation, photophobia, moderate blepharospasm. Hyperemia is expressed in all parts of the conjunctiva, spreading to the lacrimal caruncle, the semilunar and lower transitional fold.
Catarrhal form
It occurs with minor local inflammation: slight reddening of the mucous membrane of the eye, moderate amount of discharge. The course of catarrhal adenoviral conjunctivitis is mild, the duration of the disease is about one week. Usually, there are no complications from the cornea.
Follicular form
Follicles can be small, pinpoint or large, translucent-gelatinous; located in the corners of the eyelids or covering the entire infiltrated and loosened mucous membrane, especially in the area of the transitional fold. Follicular reaction outwardly resembles the initial stage of trachoma, but diagnostic errors usually do not occur, since with trachoma there are no symptoms of nasopharyngitis, fever, and the rash is localized in the area of the conjunctiva of the upper eyelid.
Film form
Occurs in a quarter of cases. It occurs with the formation of thin grayish-white films covering the mucous membrane of the eye. Usually the films are delicate and can be easily removed with a cotton swab; but sometimes dense fibrinous deposits can form, fused with the conjunctiva, which are difficult to remove from the inflamed mucous membrane. After removal of the films, the exposed mucous membrane can bleed. Sometimes pinpoint subconjunctival hemorrhages and infiltrates are detected, which completely resolve after recovery.
The outcome of membranous adenoviral conjunctivitis is often scarring of the mucous membrane. With membranous adenoviral conjunctivitis, the general condition suffers: high fever develops (up to 38°C–39°C), which can last from 3 to 10 days and asthnopia. The membranous form of adenoviral conjunctivitis can be mistaken for diphtheria .
Complications
Complications of adenoviral conjunctivitis may include bacterial or astigmatism, toxic-allergic conjunctivitis , anophthalmos, dry eye syndrome , keratitis, otitis , adenoiditis, cataract , tonsillitis , ratinal abiotraphy .
Diagnostics
If adenoviral conjunctivitis is suspected, the ophthalmologist determines whether there is a history of contact with a patient with pharyngoconjunctival fever. During examination, symptoms of conjunctivitis are revealed in combination with catarrhal changes in the upper respiratory tract and regional lymphadenopathy.
Laboratory serological, cytological, and virological methods are used to isolate adenovirus. Early diagnostics of adenoviral conjunctivitis is performed using the immunofluorescence method, which allows for the detection of specific viral antigens in a smear from the mucous membrane of the eye.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is informative, detecting adenovirus DNA in conjunctival scraping. Antibodies to adenoviruses in blood serum are detected using the complement fixation reaction (CFR), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The diagnostic criterion for adenoviral conjunctivitis is an increase in antibody titer by 4 or more times. In order to isolate and identify adenovirus on cell culture, a bacteriological study of a smear from the conjunctiva is carried out.
Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis
Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis is carried out on an outpatient basis, using antiviral agents. Locally, instillations of interferon and deoxyribonuclease in drops are prescribed 6-8 times a day during the first week of the disease and 2-3 times a day during the second week. As an antiviral therapy, ointments are also used for the eyelids (tebrofen, florenal, bonafton, riodoxol, adimal).
Antihistamines are indicated until complete clinical recovery from adenoviral conjunctivitis. Artificial tear substitutes (for example, carbomer) are used to prevent the development of xerophthalmia.
How to prognose and stop the disease
In most cases, the disease stops with complete healing of the eyes in around 2-4 weeks. As dry eye syndrome ,astigmatism, develops, using tear substitutes for a long time becomes necessary.
The best way to prevent conjunctivitis caused by adenoviruses among a group is to quickly isolate those with the virus, good ventilation, regular cleaning and encourage hygiene. All areas in the ophthalmologist’s office should be sterilized, including pipettes, eye sticks and other equipment, also with disinfectants and quartz. Swimming pools must be chlorinated according to the latest regulations.