Defination
Dengue Fever stays a biological poison passed through leeches.
Previously, infected insects were found mainly in tropical equatorial zones: in Asia, Africa, Latin America, and the Pacific islands. But Dengue Fever outbreaks have begun to be recorded much further north – in Europe (France, Croatia, Portugal), as well as in the southern regions of the United States. Moreover, as observations show, mosquitoes that carry this infection prefer not remote marshy areas (like, for example, malaria ), but urban and suburban areas.

Every single year, out of bed to 401 billion individuals become infested with dengue. WHO experts believe that the fever threatens half of the world’s population: over the past 20 years, the number of cases of the disease has increased more than eightfold. Therefore, everyone should know about dengue. At least in order to track the symptoms in time and consult a doctor.
Why is dengue fever dangerous?
Most often, nothing. The dengue virus has several serotypes (variations), and most of them cause only mild discomfort. But certain types of the pathogen can cause a serious complication – severe dengue fever. It is also called hemorrhagic fever.
The Greek word haimorrhagia means “bleeding.” In the hemorrhagic form, blood vessels become permeable, blood plasma begins to leak into other tissues, and plated levels drop sharply . All this can lead to dangerous internal bleeding, shock, organ failure, and ultimately death.

The problem is that it is impossible to predict in advance which dengue serotype a person will encounter. Each case of the disease is a roulette.
How to recognize dengue fever
Most people are lucky: the disease goes away without symptoms. Dengue symptoms appear in every fourth infected person and most often resemble the flu:
- High temperature – up to 40 °C.
- Headache.
Severe pain in muscles, bones or joints. By the way, the symptom is encrypted in the word “dengue” itself – it is a distorted English word “dandy”. The disease was named so because of the characteristic gait of the infected
- person. A person experiencing pain in muscles and joints moves unnaturally, throwing his legs forward and waving his arms, like a caricatured “dandy”.
- Feeling of pain behind the eyes.
- Swollen tonsils.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Skin rash.

Typically, the infection makes itself known 4-10 days after the bite of an infected mosquito, and symptoms last for about a week.
Nearby single cutting-edge 25 persons who contract dengue develops a severe, hemorrhagic form of the fever.
The first signs of an incipient complication appear 1–2 days after the temperature has subsided. They include :
- severe abdominal pain;
- frequent vomiting – at least three times a day;
- bleeding from the nose or gums;
- traces of blood in uarin , stool or vomit;
- bruises that appear on their own (this is a sign of subcutaneous hemorrhages);
- difficult in heavy breathing;
- anxiety, irritability;
- weakness.
- Heart problems such as heart failure , arrhythmia and other vascular diseases.
When you need to see a doctor urgently
It is worth consulting a physician in any case if you have recently visited an area where cases of dengue have been recorded and you have a fever.
Call emergency medical help immediately if fever is followed by severe abdominal pain, vomiting , or any bleeding.
How to treat dengue fever
Like most viral infections, dengue has no cure . Doctors only prescribe symptomatic therapy to alleviate the condition and help the body cope with the disease on its own.
How to treat mild dengue
Doctors give the same recommendations as for the flu or a cold :
- Take sick leave and rest more.
- Towards diminish the disease and release agony, take paracetamol-based medications. Note: ibuprofen and acetylsalicylic acid medications are contraindicated for dengue!
- Drink more liquids: water, tea, compotes, fruit drinks. You would effort sports munchies that remain supplemented with electrolytes too. It helps stop you from becoming dehydrated. Keep an eye on your health. Should symptoms show that there are complications, head to the emergency room immediately.

How to manage the care for severe dengue
Solitary fashionable infirmary also expressly exhaustive care units .
What doctors do in this situation:
Monitor your blood pressure so it doesn’t get too low.
• Variety indisputable you pick-me-up plenty of waters.
A person suffering from hemorrhagic dengue should be given fluids and electrolytes through a vein.
If it is safe to do so, stop the bleeding immediately.
If you are unable to do the other option, perform a blood transfusion.
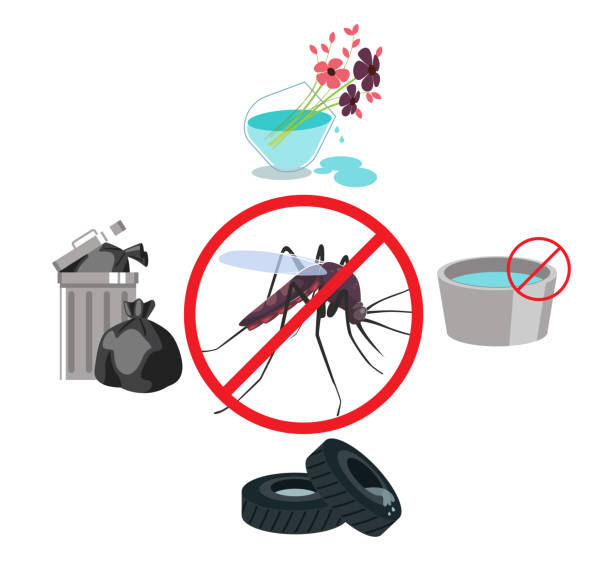

How Can You Avoid Dengue Fever
Staying away from mosquito bites is the key thing to do, including in areas that are currently experiencing dengue cases.

WHO experts recommend :
- Use repellents.
- Wear long sleeves.
- During the period of mosquito activity, if possible, stay in closed ventilated rooms. Dengue-carrying insects are most active from dawn to dusk, but can also bite at night.
- Vacation gone since bodies of water and bottles with stagnant water. There are especially many mosquitoes in such places.
It should be noted that there is a vaccine against dengue: it is administered in three doses over the course of a year. But there is a nuance. The drug is approved only for people aged 9–45 who have already had the fever. For those who are not familiar with dengue, such a vaccination can increase the risk of a severe form of the disease.
Risk factors
The chance of unindustrialized unadorned dengue is increased by a times past of DENV pollution.
Suburbanization facilitates the communication of dengue through a selection of social and environmental factors such as population density and mobility & availability of reliable water supplies, water storage practices, etc.
The risk of dengue spread at the local level also depends on the level of knowledge and attitudes and behaviour of the population about dengue, as well as the implementation of planned vector control activities in a particular locality.
Therefore, as the climate in tropical and subtropical areas changes and vectors may adapt to new environmental and climatic conditions, the scale and geography of disease risks may change.
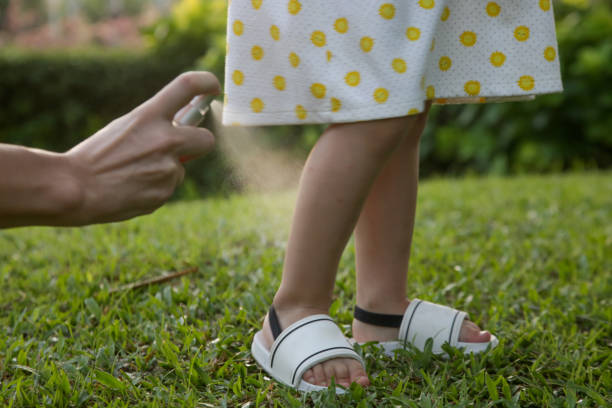

Prevention
Mosquitoes that spread dengue are most active during the daytime.
To reduce the risk of infection during a visit to tropical countries precautions should be taken.
First of all, you should be wary of mosquitoes, wear light-colored clothing that covers your body as much as possible when walking, use personal protective equipment that repels insects (repellents) in the form of sprays and creams, use fumigators in closed spaces (hotel rooms), use mosquito nets on doors, above the bed and on windows, and store drinking water in closed containers.
People who have previously had dengue fever and are planning to travel again to an endemic area, given the increased risk of developing severe dengue fever, should be especially careful and be sure to use all measures of protection against blood-sucking insects.

If you feel unwell after returning from areas where dengue fever is endemic.You should immediately consult a doctor and report visiting such countries.