Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a or chronic swelling of gum. The pathological process develops frequently. It is accompanied by discomfort: bleeding gums, pain and itching, burning in the problem area. The disease instigates against the circumstantial of deficient verbalized sanitation. It is constantly progressing. Without sufficient treatment, it develops into more dangerous forms. It is also possible to develop secondary pathological processes, including periodontitis, periodontitis and even more dangerous disorders. For example, periostitis or osteomyelitis, provided that the patient has immunodeficiency.
Diagnosis and treatment of the pathological process is carried out under the supervision of a dentist-therapist or a periodontist (a specialist in a narrow field).

Causes of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is based on an inflammatory process that is localized in the gum area. In the overwhelming majority of cases, the disease develops against the background of insufficient, poor oral hygiene. According to our estimates, gingivitis is much more common than you might think. In one form or another, the disease is diagnosed in almost 20% of people under 40. After 40, this figure increases significantly. Initial or moderate forms of gingivitis are found in almost 65% of people.
With age, the pathological process develops in an increasing number of patients; by the age of 80, the disorder occurs in almost 95% of patients, even with high-quality oral hygiene. At the same time, gingivitis and periodontitis are several times more common than caries and periodontitis among the causes of tooth loss.
Determining the exact cause of gingivitis is a prerequisite for prescribing competent treatment. Also for developing secondary prevention measures. To prevent tooth dislocation of the pathological process after the main course of therapy.
Immediate causes of the disease
The development of the inflammatory process is caused by several reasons.
The leading and maximum common is deprived oral sanitation. Plaque accrues and converts an model education ground for bacteriological flora. Most often, the inflammatory process develops due to:
- spirochete;
- Germs negative rods
- cocci (staphylococci and streptococci, and there are different types of representatives of this flora, all of them are potentially dangerous and belong to pathogenic or opportunistic flora).
The disease develops gradually. Basically, it takes more than one month or even more than one year of insufficient oral hygiene for the pathological process to begin.
Another possible cause of the pathological process is a change in the composition of saliva. For example, hormonal group, antibiotics, and chemotherapeutic drugs. Changes are also possible due to disturbances in the concentration of certain hormones. In case of endocrine pathology or as a result of natural physiological processes (the pathological process often develops during menopause, during pregnancy, or as a result of the peculiarities of the menstrual cycle).
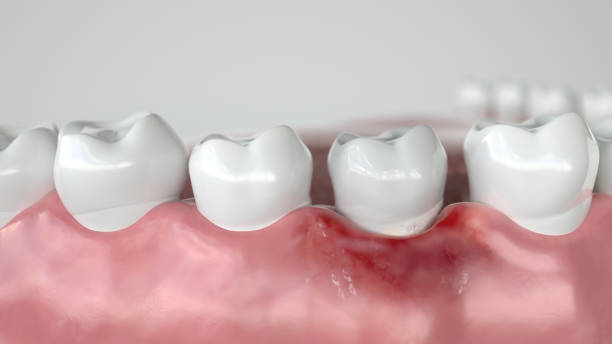
The third direct cause is decreased saliva production. It is possible against the background of salivary gland pathologies or the same hormonal imbalance.
Important!
In some cases, the patient’s disease develops as a result of a combination of several causes at once. In this case, each requires its own solution. The therapy process becomes more complicated, requires more time and effort. There are still no alternatives to therapy. The pathological process progresses slowly but steadily. How soon it will provoke complications is a matter of time.
Pathogenesis of the disorder
The pathogenesis of tissue damage around the tooth and gum inflammation depends on the specific cause of the pathological condition.
If we are talking about insufficient oral hygiene as a basis, the mechanism of development of the disorder includes several links:
- active accumulation of plaque, including under the gum;
- the formation of tartar, as a result of which gram-negative bacteria actively multiply, which require an oxygen-free environment to function;
- local inflammation develops as an attempt by the body to stop the infection and fight bacterial agents;
- Due to the dystrophic process and direct swelling, the annihilation of resin tissue inaugurates, periodontal pockets are formed, plaque also accumulates in them, and the process worsens.
As a result, gingivitis becomes chronic and a person’s constant companion. Numerous complications arise.Other disorders have different pathogenesis. But in essence it is the same. Difficulty in the production & composition of saliva contribute to the active growth of bacteria. Simply because it does not perform its functions. It does not destroy bacteria and does not prevent the development of plaque. Knowing the pathogenesis, it is much easier to fight the disease.
Factors of increased risk of development
In addition to the direct causes of gum inflammation, there are so-called risk factors. They increase the likelihood of the pathological process, but do not cause the disease themselves. Among them:
- diabetes mellitus, a major endocrine disease that affects, among other things, the condition of the patient’s oral cavity;
- hormonal imbalances of a different nature, physiological or pathological;
- avitaminosis, a state of complete absence of a particular vitamin in the body;
- hypovitaminosis, partial absence, deficiency of a certain vitamin;
- Gum injuries can become a trigger for the development of a pathological process, an entry point for infection, especially if the disease is not treated in a timely manner;
- a burdened family history, the likelihood of gingivitis, if someone in the family suffered from gingivitis or periodontitis, is significantly higher.
The majority of risk factors are modifiable. That is, they can be corrected.

Classification and forms of gingivitis
The classification of the pathological process is carried out according to several criteria.
Depending on the course of the disorder, there are two main types of disorder:
- acute gingivitis, accompanied by sharp symptoms of inflammation, the disease proceeds with characteristic clinical symptoms, requires urgent treatment to avoid complications;
- Chronic inflammation is accompanied by moderate symptoms or proceeds without them, while from time to time there are episodes of exacerbations, when the clinical picture corresponds to that of the primary acute form of the disorder.
The division is carried out according to the nature of the changes that are typical for gingivitis.
The most common form of the inflammatory process is the catarrhal form. Such gingivitis proceeds without pronounced changes. There is swelling, there is pain syndrome. But with proper treatment, the disorder can be completely dealt with.
Hypertrophic gingivitis develops with a long-term course of the pathological process. This form of the disorder received its name due to the active growth of granulation tissue in place of healthy gum structures. Sometimes the tissue grows so much that it covers the crown of the tooth.
In an aggressive course, if the infectious flora is active or the immune system fails, an ulcerative form of inflammation often develops. The disease is fractured with secondary forms of deeper infection. Without sufficient therapy, ulcerative gingivitis can develop into a necrotic form. In this case, the disease is extremely dangerous. It can be cured by surgical intervention, and then conservative correction. This is long and difficult.
Dentist-therapist Said
Classification is also carried out by stages of the pathological process. At the first stage, we are talking about complete compensation of the condition. Symptoms are minimal. Erosions, ulcers, and necrotic areas are usually absent. Although in patients with immunodeficiency, the first signs of complex forms of gingivitis are possible already at this point. Then the infectious disease moves to the 2nd, subcompensated stage. The disease responds well to therapy, but it requires more time and effort. Finally, decompensation occurs. Total inflammation of the entire gum develops. According to our estimates, complications often develop at this stage. The inflammatory process affects other structures, the periodontium, periodontium. It provokes secondary inflammations that aggravate the course of the primary disease.
Symptoms of gingivitis
Gingivitis as a disease of the oral cavity manifests itself in very different ways. Depending on the degree of expression, stage of the pathological process. The most vivid clinical picture develops at stages 2-3 of the pathology in the acute course.
pain in the oral cavity, intensifies when touching the affected gum, eating hard food, the pain also becomes stronger when brushing teeth, the pain usually develops in periods: then there is, then there is not;
- swelling, usually significant, extends not only to the affected gum, but also to the structures of the dental system surrounding the tooth;
- redness of the mucous membrane of the gum, hyperemia develops due to active blood flow and local inflammation;
- bleeding, at first minor, then more and more pronounced, at the initial stage only with active physical impact on the tissues around the tooth, then spontaneously, blood can be noticed when brushing teeth, as well as when eating hard fibrous foods;
- bad breath is the result of plaque formation, active reproduction of bacteria in the oral cavity, it is impossible to cope with it using standard hygiene methods, it returns very quickly;
- itching, burning sensation in the gums is a symbole of bruxim .
Signs of gingivitis can be more specific. Thus, with the erosive form, erosions and ulcerative defects form on the gums. With necrotic lesions, the gums are covered with a yellowish-gray coating with a sharp putrid odor.. Gingivitis of different forms requires a different approach to therapy.
Chronic gingivitis in the remission phase is almost never accompanied by any symptoms. Edema and redness after mechanical impact on tissues are possible. Periods of remission are followed by exacerbations. During the exacerbation period, the clinical picture is the same as in the acute pathological process.

Complications of the pathological process
If the course of gingivitis is constant, treatment is not carried out sufficiently (or not carried out at all), complications almost always develop. Among the possible negative consequences:
- periodontitis, an inflammatory process of the periodontium, the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth that holds it in a normal position;
- periodontitis, if periodontitis is characterized by a relatively superficial tissue lesion, with periodontitis the root tissues become inflamed, this is a much more dangerous pathological process;
- caries, since a large number of bacteria develop under the gum, cervical caries most often forms, which requires immediate treatment;
- there is a risk of the infection spreading to the periosteum and the bone itself, and, accordingly, periostitis and osteomyelitis develop; these are quite rare, but still possible complications of the pathology, especially with an aggressive course of the disease and the presence of immunodeficiency in the patient;
- Ultimately, tooth loss is possible, and if the disease spreads its influence over large areas of tissue – many teeth, prosthetics will be required.
Prevention of gingivitis complications requires timely treatment of the pathological process. Action should be taken immediately after the disorder is detected.
Diagnosis of gingivitis
The examination is carried out using several methods. Among them:
- collecting anamnesis allows us to determine the probable etiology of gingivitis, the nature of the pathological process, assess the severity of the disorder and other parameters important for prescribing appropriate treatment;
- examination, visual assessment of the condition of the gums, periodontium, an experienced doctor can determine the inflammatory process and its consequences based on visual data;
- assessment of special indices that show the level of cleanliness of the oral cavity, the degree of inflammation, etc.;
- measurement of the depth and number of periodontal pockets.
This is usually enough. Specialized laboratory tests are performed if necessary. The more tissues are affected by gingivitis, the more severe it is, the easier it is to assess. In some cases, the disease has to be differentiated from other diagnoses. Periodontitis, periodontitis and others. Differential diagnostics is also the doctor’s job.
Treatment of gingivitis
Treatment for adults and children is carried out depending on the form and stage of the pathological process. Acute gingivitis requires professional oral hygiene. Cleaning is carried out in the office of a dental hygienist. Soft plaque is removed, and hard dental deposits, which are especially dangerous, are also removed using an ultrasound technique. Especially if they have been there for a long time, since it is impossible to remove them on your own.
After hygiene, antiseptic drugs are prescribed. If the pathological process is mild, they are sufficient. If the course is moderate or severe, antibiotics are additionally indicated. They are prescribed after assessing the contents of periodontal pockets, or broad-spectrum antibacterial agents are used. Which will be effective against gram-negative bacteria, among other things.
Please note!
Physiotherapy may be performed. It is prescribed after the acute inflammatory process has been stopped. It includes electrophoresis, UHF and other methods. They help to consolidate the result, prevent complications and relapses. Specific procedures are determined by a specialist doctor.
Treatment of acute gingivitis at an advanced stage is carried out using surgical techniques. In most cases, direct excision of periodontal pockets is performed with subsequent suturing of the treated area. With an increase in tissue volumes, the appearance of granulation tissue, removal of excess gum is indicated.
Handling of gingivitis is about the equivalent chore. The same measures are taken. But in addition, the patient is prescribed immune response stimulants or interferon drugs. They are needed to suppress pathogenic microorganisms that live in the oral cavity. Chronic gingivitis is problematic to cure. But it is possible to achieve high-quality remission and keep the disease under complete control to avoid complications.
Prognosis and prevention of pathology
The prognosis depends on the type, form of the pathological process, the moment of treatment initiation, the patient’s body characteristics and many other factors. Acute gingivitis is well treated even at an advanced stage. Especially in the presence of complications.
Anticipation includes several measures:
- giving up bad habits, cigarettes and alcohol;
- quality nutrition, normalization of diet;
- high-quality oral hygiene 2 times a day;
- Unvarying preventive dental checks.
If the edges of the gums are already inflamed, there are characteristic symptoms, perhaps not clearly expressed – you need to immediately contact a doctor. Gingivitis is perfectly treatable at the initial stage. But the more time passes, the more difficult the situation becomes.